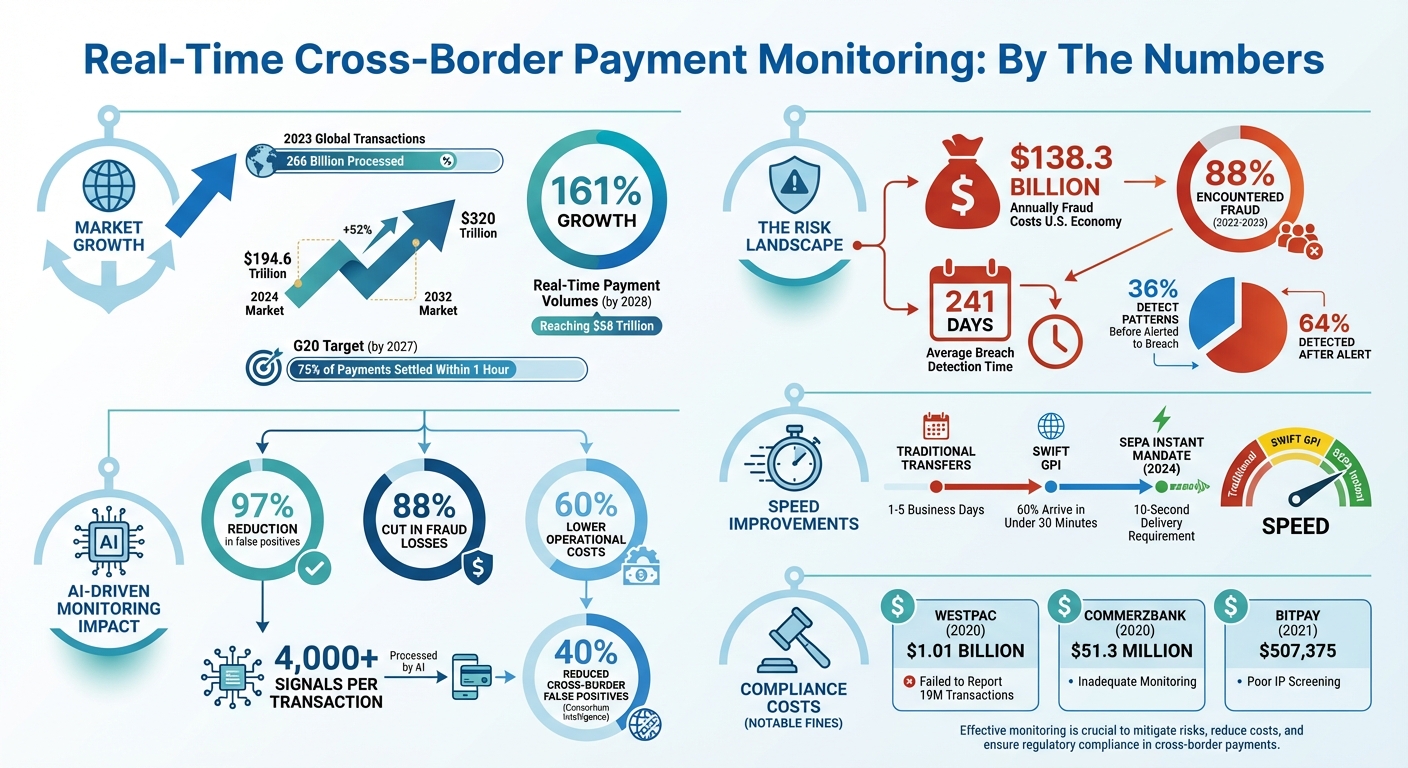
Real-time cross-border payments are growing fast, with over 266 billion transactions processed globally in 2023. But this speed brings risks like fraud, regulatory challenges, and currency volatility. Without effective monitoring, businesses face financial losses, fines, and damaged trust.
Here’s how modern systems can help:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Detect fraud and compliance issues instantly using AI and advanced tools.
- AI-Driven Detection: Reduce false alerts by up to 97% and fraud losses by 88%.
- ISO 20022 Standards: Use structured data for better accuracy and faster processing.
- Dashboards: Track key metrics like false positives, blocked transactions, and compliance rates.
- Credit Insurance Integration: Protect against customer defaults and financial disruptions.
With proper monitoring and automation, businesses can secure transactions, lower costs, and improve cash flow. These systems are essential as global regulations tighten and real-time payments become the norm.
Cross-Border Payment Monitoring: Key Statistics and Impact Metrics
The Future of Cross Border Payments
sbb-itb-b840488
Key Risks in Cross-Border Payments
Understanding the risks involved in cross-border payments highlights why modern, real-time systems are so essential. These payments face challenges that can lead to operational and financial setbacks. Key risks include fraud, regulatory hurdles, and currency fluctuations.
Fraud and Cybersecurity Threats
Fraud is a massive issue, costing the U.S. economy $138.3 billion annually. Some of the most prevalent methods include synthetic identity fraud (where fake identities are created using both real and fabricated details), Business Email Compromise (BEC), Authorized Push Payment (APP) fraud, Account Takeover (ATO), and even Fraud-as-a-Service (FaaS).
The complexity of international payments gives fraudsters opportunities to exploit vulnerabilities. With funds moving through multiple banks across different time zones, criminals can manipulate payment instructions or impersonate legitimate entities. Without real-time monitoring, fraud is often discovered only after settlement, making recovery nearly impossible.
Regulatory and Compliance Challenges
Cross-border payments must navigate a maze of regulations, including frameworks like FATF, EU PSD2/GDPR, and U.S. OFAC/FinCEN. These rules can impose operational difficulties and hefty penalties. For example:
- In September 2020, Westpac was fined approximately $1.01 billion (AU$1.3 billion) for failing to report 19 million cross-border transactions.
- That same year, Commerzbank faced a $51.3 million fine from the UK FCA for excluding high-risk countries and clients from its monitoring system.
- In February 2021, BitPay was fined $507,375 by OFAC for inadequate screening of IP addresses linked to sanctioned jurisdictions.
Regulations also demand meticulous record-keeping. Most jurisdictions require institutions to maintain transaction logs and monitoring data for at least five years, adding another layer of complexity.
As a joint statement by The Clearing House Payments Co., LLC and the Wolfsberg Group emphasizes:
"Financial institutions should not omit, delete, or alter information in payment messages or orders for the purpose of avoiding detection of that information by any other financial institution in the payment process."
- The Clearing House Payments Co., LLC and the Wolfsberg Group
Currency Volatility and Payment Delays
Currency conversion creates timing and financial risks, especially when dealing with less common currencies. Delays occur because sourcing liquidity for these currencies often takes extra time. Additionally, batching foreign exchange (FX) processing can slow down transactions.
The rise of instant payment systems adds another layer of urgency. As one payment provider explains:
"Currency exchange adds its own complications: the conversion has to be priced, executed, and confirmed in the same instant as the payment."
These delays can force businesses to hold extra cash reserves or rely on credit to cover timing gaps, which shortens their working capital cycles. While traditional international transfers generally take one to five business days, nearly 60% of SWIFT GPI payments now reach recipients in under 30 minutes when proper monitoring and data standards are applied. However, without real-time visibility, managing cash flow effectively becomes a major challenge.
These risks emphasize the importance of robust, real-time systems for monitoring and managing cross-border payments, which will be further explored in the next section.
Best Practices for Real-Time Cross-Border Payment Monitoring
To address the challenges of real-time cross-border payment monitoring, these targeted practices can help ensure both compliance and security.
1. Use Real-Time Sanctions and PEP Screening
Every cross-border payment should be screened against up-to-date sanctions and Politically Exposed Persons (PEP) databases. This includes verifying details of the sender, receiver, and any intermediary institutions – such as names, addresses, and Bank Identifier Codes (BIC).
Timeliness is key. For instance, in September 2020, MidFirst Bank processed 34 payments worth $604,000 for individuals who had just been added to the OFAC SDN List. Five of these transactions occurred within six hours, leading to an OFAC Finding of Violation.
SWIFT’s screening tools pull data from over 80 regulatory sanctions lists. When choosing a vendor, ensure their updates are frequent – daily updates are no longer enough in today’s fast-changing geopolitical climate.
For high-risk alerts, implement a "four-eyes" review process. This requires a second user to approve or block flagged transactions. Coupled with precise screening, advanced anomaly detection can further enhance security.
2. Use AI-Driven Anomaly Detection
Traditional rule-based systems, which focus on static thresholds like transaction amounts or specific countries, often fail to detect complex fraud schemes. AI-driven systems analyze over 4,000 signals per transaction, learning patterns to identify anomalies that rules alone might miss.
By adopting AI-native behavioral scoring, organizations can reduce false positives by up to 97% and fraud-related chargebacks by 88%. These systems combine conventional controls with machine learning to uncover signs of fraud, such as unusual transaction timings, irregular beneficiary patterns, or deviations from normal business hours.
"AI-Native Behavioral Scoring processes over 4,000 signals per transaction, swiftly adapting to evolving fraud tactics." – Fraud.net
Configure AI systems to block suspicious transactions until they are manually reviewed. Additionally, use consortium intelligence, which shares fraud insights across global networks, to cut cross-border false positives by up to 40%.
To streamline operations, maintain "allow" and "forbid" lists for specific accounts, automatically flagging high-risk transactions while allowing legitimate ones to proceed. Structured messaging can further improve transparency and reconciliation.
3. Adopt ISO 20022 Standards for Better Transparency
The payment industry’s shift to ISO 20022 messaging standards brings richer, more structured data fields compared to older formats. These improvements enhance screening accuracy by clearly differentiating sanctioned entities, like individuals or banks, from generic terms like country names or addresses. This approach, often referred to as "Smart Screening", reduces unnecessary alerts triggered by legitimate transactions.
Structured data also speeds up processing – a critical factor with regulations like the 2024 SEPA Instant Credit Transfer mandate, which requires payments to be delivered within 10 seconds. Nearly 60% of SWIFT GPI payments now reach recipients in under 30 minutes, thanks to these improved data standards. The detailed data fields also allow AI systems to make more precise risk assessments, cutting down on false positives while maintaining security.
4. Create Dashboards for Key Performance Metrics
Real-time monitoring becomes effective only when you can clearly see the data. Dashboards offer instant visibility into payment performance, compliance metrics, and potential risks. Key metrics to track include straight-through processing rates, average screening times, false positive rates, blocked transaction volumes, and sanctions hit rates.
A network-wide perspective is invaluable. By analyzing pseudonymized account-level data from global networks like SWIFT, businesses can identify anomalies that might go unnoticed at an individual institution level. This helps distinguish between genuinely suspicious behavior and legitimate but unusual transactions.
Automated reporting features can save time by drafting Suspicious Activity Reports (SAR) or Suspicious Transaction Reports (STR) based on flagged anomalies. These tools ensure audit-ready documentation and reduce investigation time. Additionally, since most jurisdictions require retaining transaction logs for at least five years, dashboards should include robust archival and retrieval capabilities.
5. Automate Compliance with Custom Risk Rules
No-code rules engines simplify the process of updating AML/KYC rules, allowing compliance teams to make adjustments without needing technical expertise. This can lower operational costs by up to 60% by reducing the burden of manual reviews.
Custom rules should reflect your organization’s risk tolerance and local regulations. For example, apply stricter matching thresholds for high-risk regions while allowing more flexibility for lower-risk areas. Suppression rules can automatically clear common false positives based on specific criteria, such as destination, currency, or known safe entities.
Before rolling out new rules, use simulation tools to assess their impact on alert volumes using historical data. This helps prevent overwhelming alerts or missing critical risks.
Combining Monitoring with Credit Insurance for Risk Protection
How Credit Insurance Protects Cross-Border Transactions
Real-time monitoring is excellent for spotting fraud and irregular payment activities, but it doesn’t shield businesses from the financial fallout of customer defaults. That’s where credit insurance steps in. By covering up to 90% of unpaid debts caused by buyer insolvency or political disruptions, credit insurance fills the gap when preventive measures aren’t enough. Together, monitoring and insurance form a solid defense: monitoring reduces immediate risks, while insurance cushions the blow when things go wrong.
Consider this: it takes an average of 241 days for organizations to identify and contain a breach. During this time, fraudulent transactions or account takeovers could lead to non-payment. Credit insurance acts as a safety net, protecting your accounts receivable even when monitoring systems are tested by sophisticated threats.
For nearly two decades, Macsteel has relied on this dual approach – combining credit insurance with real-time monitoring via the Coface Risk Dashboard. This setup helps them track global exposure, evaluate partner performance, and adjust risk terms quickly.
"Trade credit insurance policy helps in identifying early warning signals of potential payment difficulties. When signs indicate your customer is experiencing financial difficulty, Coface will notify you on the increased risk and establishes an action plan to mitigate and avoid loss." – Coface
This layered strategy not only safeguards businesses but also paves the way for using monitoring data to fine-tune insurance coverage.
Using Monitoring Data to Improve Insurance Coverage
Real-time monitoring doesn’t just protect against losses – it also strengthens your position with insurers. By showcasing effective risk management, you can influence credit insurance decisions. For instance, leading credit insurers process over 12,000 credit risk decisions daily using integrated data. If your monitoring system demonstrates strong fraud prevention – like reducing fraud-related chargebacks by 88% using AI-driven tools – you may qualify for better policy terms or increased coverage limits.
Take Dassault Systèmes as an example. Since 2022, they’ve incorporated Coface’s business intelligence into their customer risk management process. Their credit teams use real-time scores, sector analyses, and credit opinions alongside monitoring data to drive decisions. Monthly economic updates are shared with underwriting teams, linking monitoring insights directly to insurance strategies.
To maximize this synergy, set up automated alerts for significant financial changes in your partners, such as unusual payment patterns or behavioral red flags detected by your monitoring system. These alerts give you a chance to adjust receivables or activate your insurer’s action plan before losses occur. Using predictive scoring tools that estimate a partner’s default risk over the next year can also help insurers tailor coverage to your specific needs.
Finally, ensure your monitoring dashboards produce audit-ready logs that demonstrate compliance with sanctions screening, PEP checks, and fraud detection protocols. This documentation shows insurers that you’re actively managing risk, which can lead to more favorable insurance terms. Together, monitoring and insurance create a streamlined operation – letting your team focus on growth instead of chasing unpaid debts.
Implementation Steps and Common Mistakes
Steps for Effective Implementation
Start by identifying the payment flows that face the most delays and cause customer friction. By focusing on these areas, you can allocate resources to the corridors that will deliver the most immediate benefits. Partner with entities that are connected to local real-time payment networks and have pre-positioned liquidity in key regions. This simplifies operations by reducing the need to manage multiple banking relationships.
Adopt ISO 20022 standards to ensure each transaction carries structured, detailed data. This minimizes manual errors and enables automated compliance checks, streamlining the process. Integrating APIs into your system is another critical step. APIs allow payments to be initiated, verified, and confirmed in real time, eliminating the delays associated with batch processing systems.
Roll out the system gradually. Begin with a single payment corridor or use case to observe how real-time operations impact reconciliation and support workflows. Once the initial implementation proves successful, scale up from there. The G20 has set a goal for 75% of cross-border payments to settle within one hour by 2027. A phased approach ensures your team can adapt to these changes without being overwhelmed, aligning with the broader industry push for scalable real-time monitoring.
With these steps in place, it’s equally important to avoid common missteps that could derail your efforts.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
One frequent issue is relying too heavily on manual processes. Real-time payment flows drastically shorten the compliance review window – from days to just seconds. Manual workflows are simply too slow for this environment, and they increase the risk of missed red flags. False-positive rates for transaction monitoring alerts often range from 70% to 95%. Automating these processes is crucial to filter out false positives and allow investigators to focus on legitimate risks.
Another mistake is attempting to run real-time monitoring on legacy systems designed for outdated clearing cycles. These older systems aren’t equipped to handle the demands of 24/7 settlements or the high traffic from API integrations. Regularly updating your core banking and reconciliation systems is essential to ensure smooth, uninterrupted transactions.
Organizations also falter by keeping cybersecurity and fraud teams siloed. On average, it takes 241 days to identify and contain a breach, and only 36% of global leaders detect fraud patterns before being alerted to a breach. Merging these teams can improve coordination and create a unified response plan.
"Silos between cybersecurity and fraud teams continue to hinder coordinated payment fraud detection and prevention efforts." – Urooj Burney, Senior Vice President, Cybersecurity Payments Ecosystem, Mastercard
Lastly, neglecting to keep up with changes to ISO 20022 standards or API updates can lead to interoperability issues and blocked payments. Train your staff thoroughly on real-time transactions, as settlements now occur within seconds, requiring a new level of preparedness.
Conclusion
Cross-border payments are on track to grow significantly, with projections indicating an increase from $194.6 trillion in 2024 to $320 trillion by 2032. However, this rapid expansion comes with challenges. In the 2022–2023 period, 88% of respondents reported encountering payment fraud. This makes real-time monitoring not just an advantage but a necessity for businesses operating in global commerce. By evaluating transactions in milliseconds and stopping threats before they escalate, real-time monitoring acts as a powerful shield against fraud.
The benefits are striking: real-time monitoring can reduce fraud by 88% and lower operational costs by 60%. Automating compliance with over 26,000 global payment rules eliminates manual delays, ensuring faster, more secure cross-border transactions while minimizing the risk of regulatory penalties. Additionally, the ability to track payments from start to finish enhances visibility, enabling businesses to detect suspicious patterns early in the process.
Credit insurance serves as a critical complement to these monitoring systems. While technology can address many risks, it cannot fully protect against issues like customer insolvency, geopolitical turmoil, or extended non-payment periods. The detailed data and risk assessments provided by monitoring tools help insurers offer better terms and pricing, forming a robust risk management system. This combination allows businesses to confidently extend credit to new international clients while protecting profit margins.
The urgency of adopting these practices is underscored by the rising adoption of real-time payments. Global real-time payment volumes are expected to grow by 161%, reaching $58 trillion by 2028. Furthermore, the G20’s goal to settle 75% of cross-border payments within one hour by 2027 highlights the accelerating shift toward instant transactions. Embracing these solutions now positions businesses for faster settlements, improved cash flow, and scalable growth in an increasingly competitive marketplace.
FAQs
What should we monitor in real time for cross-border payments?
Real-time monitoring of cross-border payments relies heavily on transaction data to keep things secure and compliant. By analyzing this data, financial institutions can spot suspicious activity, meet regulatory requirements, and flag potential signs of fraud. These measures play a crucial role in safeguarding transactions and reducing risks effectively.
How do we cut false positives without missing real fraud?
To cut down on false positives while accurately identifying fraud, leverage advanced tools like AI and machine learning to better analyze patterns and detect outliers. Regularly update and fine-tune detection scenarios, review system settings, and adjust models to stay ahead of ever-changing fraud tactics. Pairing AI with high-quality data and more efficient investigation workflows helps focus on real threats, reducing unnecessary alerts and improving overall efficiency.
Why does credit insurance matter if we already monitor payments?
Credit insurance plays a key role in protecting your business, even if you’re already monitoring payments. Why? Because it adds an extra layer of security against potential risks like non-payment, customer insolvency, or even unexpected political events. Beyond just managing risks, it helps safeguard your cash flow, giving you the confidence to seize new financial opportunities and support your business’s growth.