Machine learning is transforming fraud detection in credit insurance by enabling faster, more accurate identification of fraudulent claims. Traditional methods often take weeks or months to investigate, while machine learning systems analyze vast datasets in real-time, uncovering patterns that manual processes miss.
Key insights:
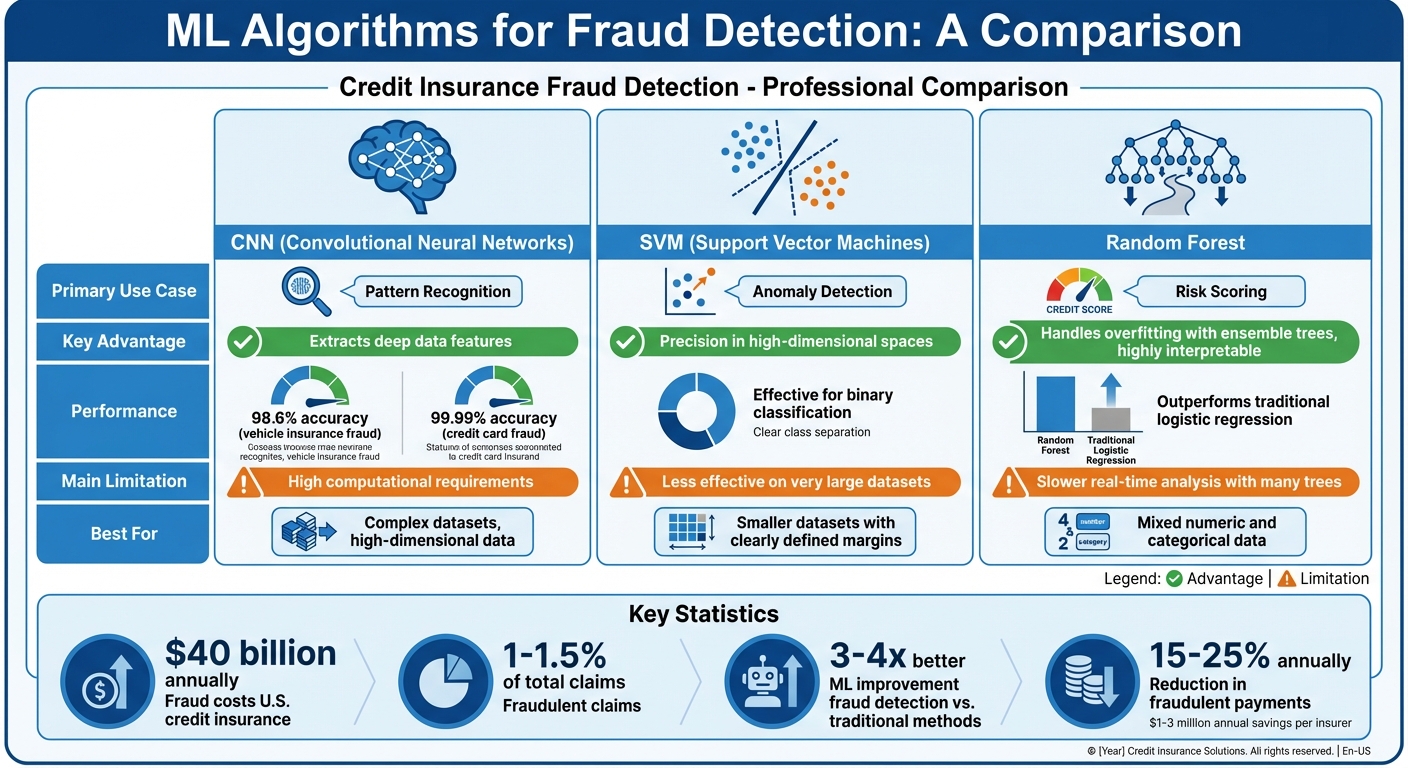
- Fraud Costs: Fraud in credit insurance costs the U.S. $40 billion annually, with 1-1.5% of claims being fraudulent.
- Efficiency Gains: Machine learning reduces false positives and automates claim reviews, saving insurers millions of dollars.
- Algorithms in Use:
- CNNs: Great for recognizing complex data patterns but require significant computational power.
- SVMs: Effective for anomaly detection, especially with smaller datasets.
- Random Forest: Balances accuracy and interpretability, ideal for risk scoring.
- Results: Insurers using machine learning have improved fraud detection rates by 3-4 times, saving millions annually.
Machine learning not only identifies fraud but also improves operational efficiency, allowing insurers to focus resources where they’re needed most. By leveraging advanced algorithms and real-time analysis, insurers can better protect against fraud while maintaining customer trust.
Machine Learning Explained: Fraud Detection Patterns 🔍
Machine Learning Algorithms for Fraud Detection
Machine Learning Algorithms for Credit Insurance Fraud Detection Comparison
Insurers are turning to machine learning algorithms to sharpen fraud detection accuracy while cutting down on false positives. By combining various techniques like deep learning and ensemble methods, they create a multi-layered defense against fraudulent activities. These tools empower real-time, data-driven responses, significantly bolstering underwriting processes.
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) for Pattern Recognition
CNNs excel at identifying intricate patterns in complex datasets, often uncovering details that traditional models overlook. In fraud detection, they are now being used to analyze high-dimensional data, such as transaction histories and claim descriptions in credit insurance.
A study conducted in 2024 by Zhejiang Gongshang University highlighted the effectiveness of this approach. Researchers developed a hybrid model that combined CNNs with traditional machine learning classifiers. This model achieved an impressive 98.6% accuracy in detecting vehicle insurance fraud and an almost flawless 99.99% accuracy in identifying fraudulent credit card transactions.
"The core of this methodology lies in utilizing the deep features extracted from the CNNs as inputs to various machine learning models, thus significantly contributing to the enhancement of fraud detection accuracy and efficiency." – Ruixing Ming et al., Zhejiang Gongshang University
While CNNs deliver exceptional results, they come with high computational demands, which can drive up infrastructure costs. For insurers tackling sophisticated fraud schemes, though, the improved detection rates often justify the investment.
Support Vector Machines (SVM) for Anomaly Detection
SVMs are particularly effective at detecting anomalies by identifying an optimal hyperplane that separates legitimate claims from fraudulent ones in a multi-dimensional feature space. They shine in binary classification tasks, especially in high-dimensional datasets where the number of features may exceed the number of samples. This makes them a solid choice for smaller datasets with clearly defined margins of separation.
To perform well, SVMs require standardized input data – either normalized between 0–1 or adjusted to zero-mean with unit variance. For larger-scale applications, increasing the cache size (e.g., to 500MB or 1,000MB) can help speed up training times.
Random Forest for Risk Scoring
Random Forest, an ensemble learning technique, uses multiple decision trees to arrive at a final prediction by averaging their outcomes. This method is highly effective at managing both numeric and categorical data, such as transaction amounts or claim types, and is robust against overfitting.
In property insurance fraud detection, Random Forest has consistently outperformed traditional models like logistic regression. One of its standout features is interpretability – analysts can identify which factors had the most influence on decisions, making it easier to explain results to regulators and stakeholders. However, using too many trees in the ensemble can slow down real-time processing.
Each algorithm offers distinct strengths, allowing insurers to customize their fraud detection strategies based on the unique challenges they face in credit insurance.
| Algorithm | Primary Use Case | Key Advantage | Main Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNN | Pattern Recognition | Extracts deep data features | High computational requirements |
| SVM | Anomaly Detection | Precision in high-dimensional spaces | Less effective on very large datasets |
| Random Forest | Risk Scoring | Handles overfitting with ensemble trees | Slower real-time analysis with many trees |
How Machine Learning Fits into Credit Insurance Processes
Machine learning is reshaping the way credit insurance functions, especially when it comes to fraud detection. By moving from reactive investigations to predictive models, insurers can now spot potential risks much earlier – sometimes even at the claim submission stage. This marks a significant shift in operations, building on the advancements in algorithms discussed earlier.
Improving Underwriting with Predictive Analytics
Underwriting used to rely heavily on fixed criteria and manual reviews, which often took a lot of time and could be influenced by human bias. Machine learning has changed this by analyzing a mix of structured data (like financial reports) and unstructured sources (such as behavioral patterns or even satellite imagery) to create more accurate risk profiles. Techniques like gradient boosting and deep learning uncover patterns that traditional methods might overlook.
By using historical data, machine learning models can place applicants into detailed risk categories, enabling pricing that feels more tailored to their situation. Even when there’s limited fraud data, unsupervised methods like anomaly detection can flag unusual patterns effectively.
"The insurance industry has traditionally relied on a combination of actuarial science and historical data to manage risk… However, the advent of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms has introduced a paradigm shift in predictive modeling." – VinayKumar Dunka, Independent Researcher
To ensure compliance and maintain trust, insurers are increasingly adopting Explainable AI (XAI). This allows them to clarify why a particular applicant was flagged or denied coverage, making the process more transparent. These refined risk assessments also feed directly into real-time claim processing systems.
Real-Time Fraud Detection in Claims Processing
Machine learning makes it possible to evaluate claims for fraud risk as soon as they’re submitted, rather than waiting until after payments are made. Unlike rigid rule-based systems, AI uses probabilistic predictions to prioritize claims based on their likelihood of being fraudulent.
This shift has brought significant efficiency improvements. For instance, automation powered by machine learning has increased straight-through processing (STP) rates by over 20%, allowing low-risk claims to be auto-paid while reserving human experts for high-risk cases. Insurers using these systems report annual savings between $1 million and $3 million, with fraudulent payments cut by 15% to 25% annually. In the U.S., where fraud rates hover around 1% to 1.5% of claims, machine learning can improve fraud detection by 3 to 4 times compared to older methods. These systems analyze a wide range of data – structured policy details, unstructured claim descriptions through natural language processing, and even damage photos – to identify inconsistencies in real time.
"Machine learning models get better at detection the longer they’re used." – EXL Service
Insurers also set clear thresholds for risk: low-risk claims are auto-paid, medium-risk ones go to regular handlers, and high-risk claims head straight to Special Investigation Units. Single machine learning models often outperform complex ensembles when quick decisions are needed.
Using Data to Guide Policy Adjustments
Machine learning doesn’t just stop at claims processing – it also influences how policies are adjusted over time. As fraud patterns become clearer, insurers can incorporate these insights into dynamic policy terms. This represents a shift from relying on static, historical criteria to using adaptive models that respond to real-time data. Predictive analytics also help insurers anticipate seasonal trends and economic factors, improving decisions around resource allocation and financial planning. Advanced techniques like graph analysis even reveal connections between entities, enabling insurers to adjust policies or deny coverage to groups of potential fraudsters. This leads to pricing strategies that are tailored to the specific fraud or default risk of each policyholder.
Collaboration is key for implementing these approaches. Data scientists, actuaries, and industry experts need to work together to ensure models align with business goals. Robust monitoring systems are also essential to prevent models from becoming outdated as fraud tactics evolve. Additionally, resampling techniques can address the imbalance caused by the small number of fraudulent claims compared to legitimate ones.
| Feature | Traditional Approach | ML-Driven Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Data Scope | Static, historical actuarial data | Structured, unstructured, and behavioral data |
| Adaptability | Rigid, rules-based systems | Continuously learns and adapts |
| Risk Assessment | Broad categories, manual analysis | Granular, personalized scoring |
| Timing | Reactive, adjusted after losses | Predictive, identifies trends early |
Transparency remains a critical factor in this shift. Explainable AI ensures that automated decisions are not only effective but also fair and compliant with regulations. This helps address concerns about bias while maintaining strong fraud prevention measures.
sbb-itb-b840488
Benefits and Performance Metrics
Machine learning has transformed fraud detection in credit insurance by uncovering subtle patterns in massive datasets that manual processes often overlook. This technology allows insurers to detect more fraud while reducing false positives, which helps maintain customer trust.
Better Fraud Detection Accuracy
Machine learning has significantly improved the accuracy of fraud detection. For instance, in 2025, American Express used advanced Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) AI models to improve fraud detection by 6%. Similarly, PayPal enhanced its real-time fraud detection capabilities by 10% using continuously operating AI systems in the same year. These advancements highlight how machine learning adapts to counter evolving fraud tactics effectively.
"Machine learning offers a promising alternative by leveraging advanced algorithms to analyze vast amounts of transactional and behavioral data, identifying patterns indicative of fraudulent activity." – Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research and Applications
Additionally, neural networks enable incremental learning, allowing systems to update with new data without requiring a complete retraining process. This approach significantly reduces the computational resources needed.
Measuring Performance: Precision, Recall, and AUC
Fraud detection models require specialized metrics because standard accuracy can be misleading. Fraudulent transactions often represent less than 1% of total claims, meaning a model could achieve 99% accuracy simply by marking all transactions as legitimate. To address this, insurers rely on more nuanced performance metrics.
- Precision: This measures the proportion of flagged transactions that are actually fraudulent, helping reduce false positives and unnecessary investigations.
- Recall: This indicates the model’s ability to identify actual fraud cases, minimizing missed instances that could lead to financial losses.
- F1-Score: By balancing precision and recall, this metric is particularly useful when dealing with rare fraud cases in imbalanced datasets.
- AUC-ROC: This evaluates how well the model distinguishes between fraudulent and legitimate transactions, with a perfect score of 1.0 indicating ideal discrimination.
"A high precision value shows the model’s ability to minimize false positives, which are especially critical in areas like fraud detection where unnecessary investigations can be costly." – Pankaj Malik et al.
| Metric | Focus | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Precision | Accuracy of fraud flags | Reduces false positives, limiting customer friction and unnecessary reviews |
| Recall | Coverage of actual fraud | Minimizes missed fraud cases, preventing financial losses |
| F1-Score | Balance of precision/recall | Provides a comprehensive measure for datasets with rare fraudulent transactions |
| AUC-ROC | Discrimination capability | Assesses how well the model separates fraud from legitimate transactions |
Efficiency Gains and Cost Savings
Machine learning doesn’t just improve accuracy – it also boosts efficiency. By automating the review of millions of transactions, it eliminates the need for extensive manual analysis. This scalability allows AI systems to handle increasing transaction volumes without requiring a proportional increase in staff.
Real-time processing adds another layer of efficiency. Modern fraud detection systems can classify transactions in milliseconds, enabling instant decisions during underwriting or claims processing. This speed ensures quicker approvals for low-risk claims while directing expert attention to suspicious cases. The result? Faster service for honest customers and more effective fraud prevention. These advancements continue to pave the way for even more sophisticated fraud detection approaches in the future.
Future Developments in Machine Learning for Fraud Detection
Next-generation fraud detection systems are stepping up their game by blending advanced analytics, improved data security, and greater transparency. These systems aim to not only enhance accuracy but also address growing concerns about privacy. Let’s dive into some of the cutting-edge techniques driving this evolution.
Advances in Predictive Analytics
Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) are reshaping how organizations uncover fraud. By mapping relationships between entities – like borrowers, lenders, and guarantors – GNNs can detect complex patterns that traditional methods might miss. For instance, in 2023, JPMorgan Chase used GNNs to combat money laundering, cutting corporate fraud costs by 25% that year.
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are also making waves. These networks create synthetic fraud cases to balance training datasets, helping models learn from more realistic and varied scenarios. Meanwhile, Reinforcement Learning (RL) equips systems to adapt to evolving fraud tactics by learning through trial and error.
"AI models offer a data-driven, adaptive approach that goes beyond predefined rules, enabling organizations to prevent fraud more effectively." – Nilesh Jain, Researcher and Author
Combining Blockchain and Machine Learning
Securing data and fostering collaboration are just as important as predictive analytics in the fight against fraud. Blockchain technology, when paired with machine learning, ensures the integrity of sensitive transactional data. Its immutable ledger provides a transparent way to track and secure data, which is especially helpful when insurers need to share fraud signals without compromising customer privacy.
Federated Learning is another game-changer. This approach allows multiple organizations to train fraud detection models together without sharing raw data, preserving privacy and meeting regulatory requirements. By drawing on collective intelligence across the industry, it strengthens fraud detection capabilities. Additionally, blockchain’s transparent ledger ensures a clear audit trail of data inputs used in decision-making, boosting trust and accountability.
AI-Driven Fraud Prevention Systems
The future of fraud detection lies in integrating multiple AI technologies into unified systems that cover every stage of the credit insurance process. Explainable AI (XAI) is a key component, making it easier to understand how deep learning models arrive at their decisions. This added clarity helps during audits and when resolving disputes, building trust among stakeholders.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is broadening fraud detection beyond just numbers. By analyzing text – like employee emails, market reports, and policy documents – NLP can identify insider threats and unusual patterns. Additionally, incremental machine learning keeps fraud detection systems up to date by continuously learning from new, real-time data streams. This ensures they stay effective as fraud tactics evolve.
Conclusion
Machine learning has reshaped how credit insurance tackles fraud detection, offering a dynamic alternative to traditional rules-based systems. Unlike static methods that require constant updates, ML models adapt in real time – a critical advantage as global online payment fraud losses climbed to $41 billion in 2022 and are expected to hit $48 billion by the close of 2023.
This evolution from rigid rules to adaptive algorithms delivers tangible benefits. By distinguishing genuine customer activity from fraudulent behavior, ML significantly reduces false positives, maintaining customer trust while freeing analysts to address more intricate cases. Additionally, these systems handle massive transaction volumes that would be impossible to review manually, enabling businesses to scale fraud prevention without a matching increase in costs.
Key Takeaways for Business Owners
For business owners, the path forward starts with clean, diverse data and a layered defense strategy that combines machine learning, consortium data, and traditional rules. Given how quickly fraud tactics evolve, continuous retraining of models is crucial to maintain accuracy. When choosing algorithms, it’s important to strike a balance between effectiveness and interpretability – Random Forests provide clarity for compliance needs, while Neural Networks excel in spotting complex fraud patterns across high-dimensional data.
Real-time monitoring is now the industry standard. Transitioning from batch processing to instant transaction analysis allows businesses to intercept fraudulent activity before financial damage occurs. Additionally, ML’s ability to detect new and emerging fraud types gives companies a significant edge in safeguarding accounts receivable. These strategies not only improve fraud detection but also set the stage for implementing scalable, future-ready solutions.
Learning More with CreditInsurance.com
Discover how machine learning enhances fraud detection with CreditInsurance.com. From protecting against non-payment and customer insolvency to mitigating political risks, CreditInsurance.com offers in-depth resources tailored to your credit and accounts receivable insurance needs. Whether you’re seeking to expand credit lines, secure better financing, or adopt cutting-edge fraud prevention methods, their expertise is designed to help you succeed.
FAQs
How does machine learning help detect fraud in credit insurance?
Machine learning has become a game-changer for fraud detection in credit insurance, thanks to its ability to quickly analyze massive amounts of data. It can spot unusual patterns or behaviors that might signal fraud – often catching subtle anomalies that traditional methods could overlook.
Using advanced algorithms like decision trees, neural networks, and clustering techniques, machine learning models bring greater precision and efficiency to identifying fraudulent activities. This benefits businesses by reducing financial risks and creating a more secure and streamlined underwriting process.
What are the advantages of using CNNs, SVMs, and Random Forests for fraud detection in credit insurance?
Using Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), Support Vector Machines (SVMs), and Random Forests for fraud detection in credit insurance brings several benefits:
- CNNs are excellent at spotting subtle patterns and irregularities in complex datasets, making them a strong choice for identifying fraud that might slip past traditional detection methods.
- SVMs handle high-dimensional data exceptionally well, ensuring precise classification even when working with large and intricate datasets.
- Random Forests, as an ensemble model, offer reliable predictive performance and are more straightforward to interpret compared to many other machine learning techniques.
These algorithms allow businesses to enhance both the accuracy and speed of fraud detection, protecting against financial risks and reinforcing confidence in credit insurance underwriting.
How do machine learning models detect fraud and adapt policies in real time?
Machine learning models excel at spotting fraud in real time by sifting through massive data sets to identify unusual patterns or behaviors that might suggest fraudulent activity. These models leverage advanced algorithms to analyze transactions as they happen, flagging anything suspicious almost immediately.
Beyond just detection, machine learning also plays a key role in adjusting policies dynamically. By constantly learning from fresh data, these models can fine-tune fraud detection rules and suggest updates to underwriting policies. This ongoing learning process helps businesses stay a step ahead of ever-changing fraud tactics, ensuring better risk management and stronger protection for credit insurance providers.