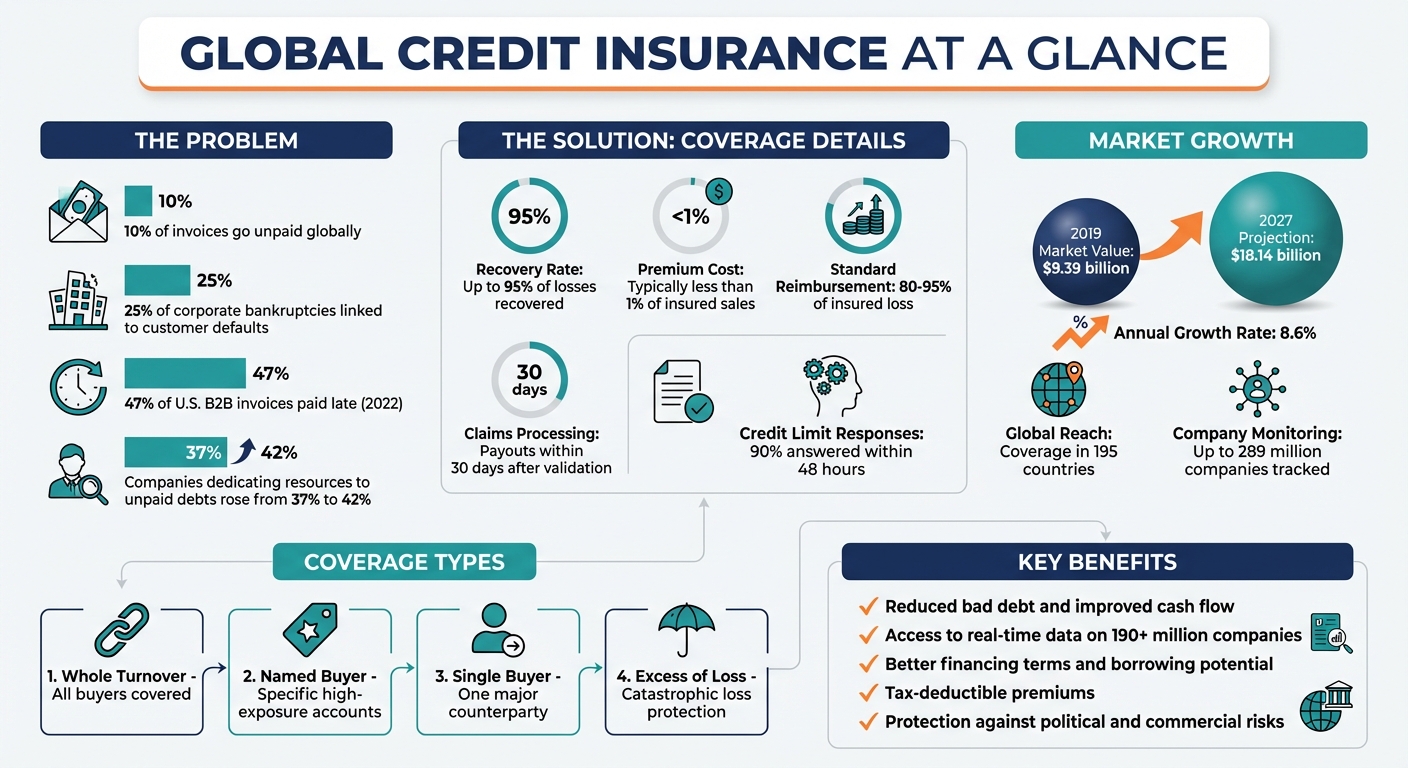
Global credit insurance helps multinational companies protect their finances from unpaid invoices, customer insolvencies, and political risks. With about 10% of invoices going unpaid globally and 25% of corporate bankruptcies linked to customer defaults, this insurance ensures businesses recover up to 95% of losses. It also improves cash flow, supports market expansion, and enhances borrowing potential by securing receivables.
Key Takeaways:
- Coverage: Protects against non-payment (due to insolvency or delays) and political risks (wars, currency restrictions, etc.).
- Cost: Typically under 1% of insured sales.
- Benefits: Reduces bad debt, accelerates collections, and provides better access to financing.
- Flexibility: Options include whole turnover, named buyer, or single buyer policies.
- Setup: Requires risk assessment, provider selection, and centralized implementation with localized support.
This solution is essential for managing cross-border financial risks and ensuring stability while pursuing growth.
Global Credit Insurance: Key Statistics and Benefits for Multinational Companies
Credit Insurance as a Risk Mitigation Tool for International Trade
Financial Risks for Multinational Companies
Expanding business across borders comes with a host of financial risks. Multinational companies not only contend with commercial challenges like customer insolvency, bankruptcy, or delayed payments but also face political risks stemming from events such as wars, terrorism, riots, or revolutions. On top of that, currency fluctuations, economic downturns, and bank failures can eat into profit margins and disrupt cash flow. Recognizing these risks is the first step toward creating effective global credit insurance strategies. Let’s break down some of the key risks in detail.
The operational toll of these challenges is immense. For instance, in 2022, 47% of U.S. B2B invoices were paid late. This not only diverts resources away from growth but also increases overhead as billing and finance teams spend countless hours trying to recover payments. For multinational companies managing operations across various countries, centralized oversight becomes critical to maintain control over global trading agreements.
Non-Payment and Customer Insolvency
Unpaid invoices can wreak havoc on a company’s finances. When a customer declares bankruptcy or simply stops paying, businesses face immediate cash flow issues, which can put a halt to planned investments. The impact doesn’t stop there – uninsured or overdue receivables can weaken a company’s overall financial health.
"Your day-to-day business involves extending credit to your clients… But it’s a practice that lays you open to the risk of default or insolvency, which together account for 25% of corporate bankruptcies."
Even customers with solid credit histories aren’t immune to defaulting. External factors like national economic crises, abrupt regulatory changes, or sharp currency devaluation can make it impossible for them to meet their payment obligations. Over the years, the number of companies dedicating resources to chasing unpaid debts has risen from 37% to 42%, highlighting how pervasive this issue has become. These payment hurdles are only exacerbated by external forces beyond a company’s control.
Political and Economic Instability
Political unrest often brings financial chaos in its wake. Events like wars, terrorism, riots, and revolutions can disrupt foreign buyers’ ability to pay, even if they are willing to do so. Governments may impose currency inconvertibility or transfer restrictions, effectively trapping funds within their borders and complicating collections. In extreme cases, trade embargoes or asset expropriation – where governments seize company property – can completely dismantle operations.
Economic instability adds another layer of complexity. Sudden currency devaluation can inflate transaction costs and shrink profit margins. Companies operating in regions prone to volatility face higher risks, making political risk insurance an essential safeguard. The importance of such coverage is reflected in the growth of the global trade credit insurance market, which was valued at $9.39 billion in 2019 and is projected to reach $18.14 billion by 2027, with an annual growth rate of 8.6%.
What Global Credit Insurance Policies Cover
Global credit insurance policies are designed to protect multinational businesses from risks that could jeopardize their receivables. These policies address two primary types of risks: commercial defaults and political uncertainties. Commercial risks include situations where customers fail to pay due to insolvency, bankruptcy, or prolonged default (typically 60–180 days overdue). On the other hand, political risks cover events like war, terrorism, riots, currency inconvertibility, expropriation, or sudden changes in import/export regulations.
Most policies reimburse between 80% and 95% of the insured loss. Beyond financial recovery, insurers provide three essential services: real-time business intelligence to evaluate buyer solvency, localized debt collection services, and swift claims processing, with payouts often issued within 30 days after validation and the required waiting period. Let’s explore how these policies extend to various sales channels and offer tailored options.
Coverage for Domestic and Export Sales
A key strength of global credit insurance is its ability to cover both domestic and international sales under one comprehensive framework. This flexibility allows multinational companies to manage risks seamlessly across multiple markets. For example, a U.S.-based business can confidently extend credit terms to a client in Germany just as easily as to one in Texas. Global agreements centralize coverage for all subsidiaries while still providing localized support, ensuring each branch benefits from tailored assistance across as many as 195 countries.
Protection Against Bad Debt and Late Payments
Coverage activates in two main scenarios: when a customer is formally declared insolvent or when payments are significantly overdue (typically after 60–180 days). Additionally, political events, such as trade embargoes or restrictions on currency transfers, can also trigger coverage. However, these policies generally exclude physical damage to goods, fraud that could have been reasonably detected, or invoices tied to unresolved commercial disputes. To maintain coverage, businesses must follow "stop-shipment rules", which require halting deliveries if a customer surpasses the late-payment threshold outlined in the policy.
Customizable Coverage Options
Global credit insurance policies are highly adaptable, allowing businesses to tailor coverage to their specific needs and strategies. Depending on the company’s goals, several policy structures are available:
- Whole Turnover: Covers all buyers, offering the most cost-effective pricing per dollar insured.
- Named Buyer: Focuses on specific accounts with higher exposure.
- Single Buyer: Targets one major counterparty or project.
- Excess of Loss: Provides protection for catastrophic losses above a set deductible.
Companies can also choose between discretionary limits, which allow some flexibility, and non-cancellable limits, which lenders often prefer as stronger collateral despite their higher premiums. These options ensure businesses can align their coverage with both operational and financial needs.
sbb-itb-b840488
How to Set Up Global Credit Insurance
Setting up global credit insurance involves a detailed process that aligns your parent company’s overall strategy with the specific needs of its international subsidiaries. This process typically includes assessing risks, selecting the right insurance provider, and implementing coverage across all locations in a coordinated manner.
Assessing Your Credit Risks
Before launching a global credit insurance policy, start with a thorough evaluation of your credit exposure in every market where your business operates. This includes analyzing the macroeconomic, financial, and political conditions in each country, along with identifying any industry-specific risks. As Coface explains, "The first step in arranging multinational credit insurance requires a global analysis of the commercial risk".
To dig deeper, apply the "5 Cs of Credit" framework – Character, Capacity, Capital, Collateral, and Conditions – to assess customer reliability. Tools like Moody’s credit insights, which cover over 460 million entities worldwide, and AI-powered solutions like the PAYCE Score, which predicts bankruptcy risk with 80% accuracy up to a year in advance, can provide valuable insights. Use centralized dashboards to get a clear picture of your global credit exposure and set up automated triggers to flag emerging risks early. Stress testing your portfolio can also reveal how it might perform under adverse economic scenarios. These insights will help you make informed decisions when selecting an insurance provider.
Choosing an Insurance Provider
When selecting a credit insurance provider, look for one that offers both a global reach and strong local expertise. Leading insurers monitor up to 289 million companies across more than 160 countries and respond to 90% of credit limit requests within 48 hours. It’s also important to check the financial strength of potential providers through their credit ratings, such as Allianz Trade’s AA rating from Standard & Poor’s or Coface’s A1 rating from Moody’s.
Technology plays a critical role, so evaluate the provider’s capabilities in areas like API integration, which can seamlessly connect their credit risk tools with your existing ERP or financial systems. Partnering with a specialized insurance broker can help you navigate the complexities of international policies and find cost-effective solutions. As a reference, premiums for standard trade credit insurance typically range between 0.10% and 0.20% of total insured sales.
Rolling Out Coverage Across Subsidiaries
Once you’ve assessed your risks and chosen a provider, the next step is implementing a unified coverage plan across all subsidiaries. A master agreement can help maintain consistent coverage globally while allowing for local flexibility. According to Coface, "We help you design the policies and services requested by your subsidiaries" and "Establish a master agreement and dedicated mechanisms to maintain consistency".
Ensure your plan complies with local insurance laws and financial regulations. You can either manage the policy centrally from your headquarters or let local entities work directly with in-country insurance teams, depending on what fits your organization best. Choose a provider with dedicated local underwriters and Global Solutions teams who can offer market-specific insights and understand regional payment practices and regulations. This balance of centralized control and localized expertise ensures your policy is both effective and adaptable to regional needs.
For additional information, visit CreditInsurance.com.
Benefits of Global Credit Insurance
Implementing global credit insurance across your multinational operations can significantly reshape how you manage finances and pursue growth.
Stronger Cash Flow and Financial Stability
Global credit insurance bolsters your balance sheet by reducing the risk of payment defaults. Knowing that a large portion of your transactions are protected allows you to manage working capital with greater ease. This policy helps reduce Days Sales Outstanding (DSO), leading to quicker collections and a more consistent cash flow.
But the benefits go beyond just protection. Credit insurance allows you to redirect funds previously tied up in bad-debt reserves. These freed-up resources can then be channeled into operations, product innovation, or market expansion. As Ori Ben-Amotz, CFO of Hadco, put it:
"Credit insurance has transformed the way we do business and make decisions".
Additionally, insurance premiums are often tax-deductible, adding another layer of financial advantage. This improved liquidity provides the confidence needed to explore new opportunities.
Facilitating Business Expansion
A stronger cash position makes it easier to explore new markets with less financial risk. When entering unfamiliar territories, credit insurance helps overcome a major hurdle. It provides access to real-time solvency ratings and economic data on millions of companies worldwide, enabling you to identify trustworthy partners and evaluate customer creditworthiness, even in regions where you lack direct experience. Leading insurers offer insights into 190 million companies across 185 countries.
Armed with this intelligence, you can confidently offer open account terms and extended payment schedules to international buyers – giving you a competitive advantage over businesses that require upfront secured payments. Furthermore, credit insurance protects against political risks such as currency restrictions, expropriation, and trade sanctions, which can otherwise derail expansion plans. With so many B2B invoices going unpaid, this protection is crucial when scaling operations globally.
Better Access to Financing
Securing your international receivables with global credit insurance doesn’t just limit losses – it also enhances your borrowing potential. Insured receivables improve your credibility with banks and lenders. When your foreign accounts receivable are insured, lenders are more inclined to include them in your borrowing base, giving you greater access to working capital. As the Export-Import Bank of the United States explains:
"Lenders are more likely to include foreign receivables and inventory in your borrowing base when those receivables are insured, giving you access to additional financing and improving cash flow".
This increased borrowing capacity often comes with better terms. Banks view insured receivables as high-quality collateral, which can lead to lower interest rates and more favorable financing conditions. And the cost of this coverage remains modest – typically less than 1% of your total insured sales – while the financial benefits can be substantial. For multinational operations, this can support complex financial arrangements like receivables securitization or pre-export working capital financing.
For more details on how credit insurance can support your global business, visit CreditInsurance.com.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of cross-border risks requires a well-rounded strategy that tackles both commercial uncertainties and political challenges. Among these, unpaid invoices continue to be a major hurdle for multinational companies. In this landscape, global credit insurance has emerged as more than just a safety measure – it’s a strategic asset that can drive growth and stability.
The numbers speak for themselves: businesses utilizing global credit insurance typically safeguard 85% to 95% of their invoice amounts. They also gain access to real-time data on 289 million companies spread across 160+ countries. On top of that, insured receivables are often viewed as high-quality collateral, leading to better financing terms from lenders. And all of this comes at a reasonable cost – usually less than 1% of insured sales. Beyond these financial benefits, companies unlock capital that would otherwise be tied up in reserves for bad debt, enabling smarter and more confident decision-making.
To truly maximize the benefits, it’s crucial to customize your coverage to fit your specific risk profile. Whether you’re looking for Excess of Loss coverage to guard against catastrophic losses, political risk insurance for ventures in emerging markets, or a centralized master agreement that supports all subsidiaries, the right approach should strike a balance between global consistency and local adaptability. Once you’ve secured the right coverage, the next step is to take action.
As you assess your company’s exposure to international trade risks, think about how global credit insurance can transform uncertainty into opportunity. Offering competitive open account terms, venturing into new markets with confidence, and securing better financing options can redefine your competitive edge on the global stage, helping you achieve your expansion goals.
For tailored solutions and expert resources designed for multinational operations, visit CreditInsurance.com.
FAQs
How can global credit insurance help multinational companies secure better financing?
Global credit insurance offers multinational companies a way to turn uncertain receivables into insured assets, which lenders are more likely to accept as collateral. By covering foreign accounts receivable, this type of insurance reduces the perceived risk for banks and financial institutions. As a result, lenders are often more inclined to extend larger credit lines or offer more favorable interest rates. Essentially, the insurer’s backing boosts the company’s appeal to lenders by lowering the risk of default.
Another advantage of a global credit insurance program is that it consolidates risks from all subsidiaries into one centrally managed policy. This unified approach not only simplifies risk management but also provides a clear picture of the company’s worldwide exposure. For lenders, this transparency makes evaluations easier and enhances the company’s financial standing. For U.S. businesses, the benefits can be tangible – such as increasing a credit facility from $10 million to $15 million. These additional funds can then be used to fuel growth, manage inventory, or address working capital needs. For more details on how credit insurance can improve financing opportunities, CreditInsurance.com offers useful insights.
What is the difference between whole-turnover and single-buyer policies in global credit insurance?
Whole-turnover and single-buyer policies offer distinct advantages depending on a business’s needs, with differences in coverage, flexibility, and cost.
A whole-turnover policy provides protection for an entire customer portfolio, giving businesses the ability to set credit limits across multiple buyers. These policies often include discretionary credit limits, meaning exporters can ship to approved customers without needing prior approval for each transaction. Typically, coverage extends up to 95% of the invoice value for private buyers and up to 100% for sovereign buyers. Upfront costs are minimal, often requiring just a refundable deposit.
On the other hand, a single-buyer policy focuses on protecting receivables from one specific customer. This option is particularly useful for businesses looking to manage risks tied to a high-value or strategically important buyer. Coverage for private buyers usually maxes out at 90%, with sovereign buyers covered at 100%. These policies come with low minimum premiums and no application fees, and deductibles can be included to keep pricing more affordable.
In summary: Whole-turnover policies are ideal for businesses needing broad protection across multiple customers, while single-buyer policies work well for managing risks tied to a single, critical account.
What steps should multinational companies take to evaluate credit risks before obtaining global credit insurance?
To effectively evaluate credit risks, multinational companies should begin by examining both their individual customers and the countries they operate in. Start by collecting essential data like audited financial statements, payment histories, and credit ratings for each buyer. Use an internal scoring system to assess key factors such as liquidity, leverage, profitability, and payment behavior. Supplement this with external data, including credit bureau reports, trade references, and broader economic indicators like GDP growth, inflation rates, and currency trends to gauge country-level risks.
Keep your risk assessments current by updating them regularly as new financial data or geopolitical events emerge. This could include developments like insolvencies or sanctions. For new customers, perform quick credit checks by reviewing credit limits, banking references, and any history of defaults. Scenario analyses can also be a valuable tool to anticipate how customer non-payment might affect your cash flow and working capital.
For a more robust strategy, consider leveraging the educational resources offered by CreditInsurance.com. These resources can help you better understand credit insurance and align your evaluations with a customized global policy. Taking this step can safeguard your business against both commercial defaults and political uncertainties.


