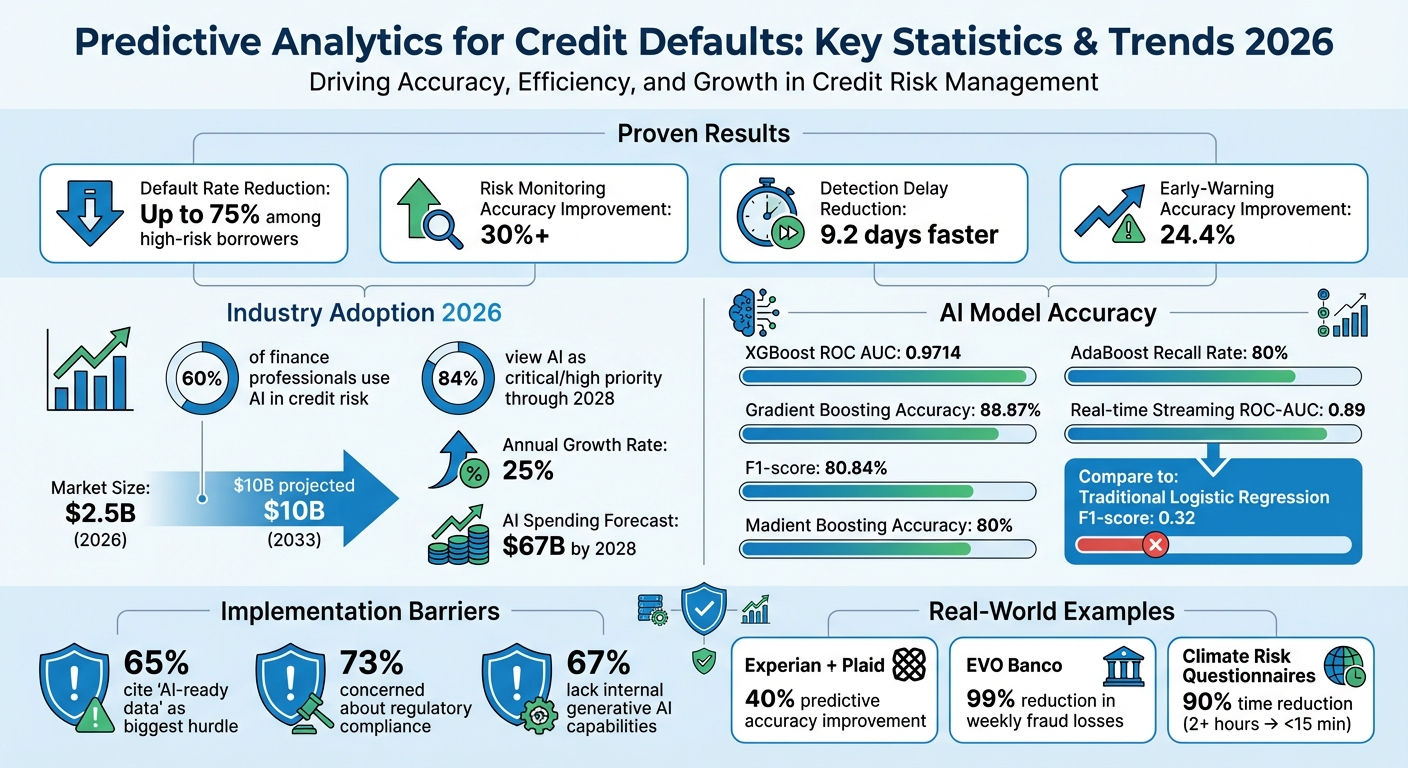
Predictive analytics is reshaping how financial institutions manage credit risk. By leveraging real-time data, advanced machine learning models, and AI-driven tools, lenders can now predict defaults with greater precision and take preemptive action. This approach has already reduced default rates by up to 75% among high-risk borrowers and improved risk monitoring accuracy by over 30%.
Key highlights include:
- Real-Time Data Integration: Continuous monitoring of borrower behavior, such as spending patterns and cash flow, enables faster and more accurate risk detection.
- Machine Learning Advances: Tools like XGBoost and Random Forest excel in identifying complex borrower behaviors, outperforming older models in accuracy and recall rates.
- Adoption Trends: Nearly 60% of financial professionals now use AI in credit risk management, with the market projected to grow by 25% annually through 2033.
Challenges like data quality, regulatory compliance, and model transparency remain, but solutions like SHAP and LIME are helping address these issues. The future of predictive analytics lies in integrating explainable AI and real-time decision-making into financial workflows.
This article explores these trends, offering actionable insights for businesses aiming to strengthen their credit risk strategies.
Predictive Analytics in Credit Risk: 2026 Adoption Statistics and Performance Metrics
Real-Time Data Integration and Streaming Pipelines
Monitoring Credit Risk with Real-Time Data
Real-time data is changing the way financial institutions manage credit risk, moving from a reactive approach to a proactive one. Instead of waiting for monthly reports, banks and lenders can now continuously monitor borrower behavior, such as payment patterns, cash flow fluctuations, and unusual transactions. This shift is crucial. As noted by Confluent staff:
By the time a batch report flagged the activity, the money had already been stolen.
For example, a 7-day sliding window streaming model demonstrated an ROC-AUC of 0.89 for predicting 30-day delinquencies across 2.7 million loan accounts. This system reduced detection delays by 9.2 days and improved early-warning accuracy by 24.4%. By analyzing "behavioral traces" – like repayment habits, app usage, and transaction patterns – these systems can quickly flag deviations from a borrower’s usual behavior, which might indicate financial stress. As Emma Li, David Thompson, and Michael Chen pointed out:
The system demonstrates the feasibility of continuous credit-risk monitoring using high-velocity behavioral data.
This capability lays the groundwork for further advancements in machine learning models aimed at predicting defaults.
Examples: Open Banking and Streaming Data
Some financial institutions have already embraced real-time streaming architectures with notable results. In August 2025, Experian integrated real-time cash flow insights from Plaid, processing over 500 million transactions daily. This integration enhanced risk assessments and expanded credit access for borrowers with limited credit histories, achieving a 40% improvement in predictive accuracy by combining cash flow data with traditional credit scores. Brian Funicelli from Experian explained:
Real-time data provides an up-to-date view of a consumer’s financial history… allowing lenders to gain deeper insight into creditworthiness.
EVO Banco in Spain also adopted a real-time architecture using Confluent (Apache Kafka) to tackle various fraud threats, cutting weekly fraud losses by 99%. Similarly, Alpian Bank in Switzerland uses Apache Kafka alongside Agentic AI to power intelligent assistants. These assistants operate within strict compliance rules, ensuring AI-driven decisions are always based on the latest operational data.
The technical backbone of these systems typically includes tools like Apache Kafka for event streaming, Apache Flink for stream processing, and feature stores such as Feast or Tecton. These tools deliver pre-computed features with millisecond-level latency, enabling fraud and credit risk assessments to be completed within 100–200 milliseconds. This speed and precision are critical for proactive credit risk management. As technology consultant Kai Waehner emphasized:
Data streaming is not just about speed. It supports data consistency, compliance, improves transparency, and reduces operational complexity.
These systems not only provide faster fraud detection but also enhance the machine learning models used for predicting defaults, making financial systems more resilient and adaptive.
Machine Learning Improvements for Default Predictions
Using Multiple Data Sources for Better Predictions
Modern machine learning models are reshaping the way default predictions are made by incorporating a variety of data sources. Traditional scoring methods, like logistic regression, mainly rely on standard financial metrics such as payment history and amounts owed. In contrast, newer algorithms integrate alternative data, including social media activity, mobile phone usage patterns, and behavioral analytics. This expanded approach is particularly beneficial for borrowers with limited or no formal credit history.
Engineered features provide a deeper understanding of borrower behavior. Instead of focusing solely on raw data, lenders now use calculated ratios – like debt-to-income or age-to-experience – to assess financial maturity and repayment ability more effectively. Additionally, leveraging text analysis from loan officer assessments, refined by large language models (LLMs), has proven to enhance default predictions. As highlighted in the European Journal of Operational Research:
Integrating text, particularly ChatGPT-refined texts, can improve the prediction of small business loan default.
Advanced ensemble methods like Random Forest and XGBoost stand out for their ability to capture complex relationships across numerous features. This level of sophistication allows these models to deliver stronger predictive results than traditional linear models, resulting in significantly lower default rates.
How AI Reduces Default Rates
Studies consistently show that ensemble methods far outperform traditional models in accuracy and reliability. For instance, Gradient Boosting models achieved an impressive accuracy of 88.87% and an F1-score of 80.84%. XGBoost delivered a ROC AUC of 0.9714, showcasing its precision. In comparison, traditional logistic regression often lags behind, with an F1-score of just 0.32 and an AUC of 0.7679.
Adrian Iulian Cristescu from NTT Data Italia emphasized this advantage:
Ensemble-type methods (Random Forests, XGBoost, and Gradient Boosting) consistently outperform the simpler models (Decision Trees and logistic regression) across the board, clearly indicating the superior ability of the former to handle complex patterns and imbalanced data.
These advancements translate into tangible results, such as lower default rates. For example, AdaBoost models have achieved recall rates as high as 80% in identifying true defaulters. XGBoost has also demonstrated exceptional performance across all segments of arrears, significantly outperforming logistic regression in these scenarios.
Challenges in Adopting Machine Learning
Despite the clear benefits, implementing advanced machine learning models comes with its own set of challenges. A major issue is class imbalance – credit datasets often have far more "good" clients than defaulters. This imbalance can cause models to underperform when identifying the minority class.
Another hurdle is the "black box" nature of sophisticated models like Deep Learning and XGBoost. Unlike logistic regression, which offers straightforward interpretability through its coefficients, these advanced models lack transparency. This can create difficulties in meeting regulatory standards, such as those outlined in GDPR and IFRS 9. To address this, financial institutions are increasingly using tools like SHAP and LIME to provide interpretability.
Data quality and standardization also pose persistent obstacles. Without standardized datasets and preprocessing methods, comparing model performance and ensuring consistent results becomes difficult. Additionally, there’s a risk that these models could amplify biases present in historical data, leading to discriminatory lending practices. To prevent overfitting – where a model performs well on training data but struggles with new cases – businesses must carefully adjust hyperparameters like lambda, max_depth, and min_child_weight.
Adoption Trends and Future Outlook
2026 Adoption Rates and Industry Data
AI has firmly established itself as a cornerstone in credit risk management, with nearly 60% of finance professionals using AI in some capacity within their departments as of early 2026. Financial institutions are no longer experimenting; they’ve fully integrated AI into their operations, delivering measurable business outcomes.
A whopping 84% of financial institution decision-makers view AI as critical or a high priority for their business strategies through 2028. Vijay Mehta, EVP of Global Solutions and Analytics at Experian Software Solutions, emphasized this shift:
AI adoption among financial institutions is accelerating, with 84% of respondents identifying AI technology as being critical or a high priority for their business strategy over the next two years.
The numbers back this up. The AI-driven credit scoring market has grown to $2.5 billion in 2026, up from $2.0 billion in 2025, with a projected 25% annual growth rate through 2033, potentially reaching $10 billion. Additionally, financial services firms are forecasted to spend over $67 billion on AI by 2028.
However, challenges remain. 65% of leaders cite "AI-ready data" as their biggest hurdle, while 73% express concerns about regulatory compliance. Diana Rothfuss, Global Solutions Strategy Director for Risk, Fraud & Compliance Solutions at SAS, highlighted the industry’s evolution:
The industry has matured beyond the proof-of-concept, and the banks that succeed will be those that industrialize their AI to turn pilots into profit and governance into competitive advantage.
These developments are paving the way for deeper integration of predictive analytics into financial intelligence systems.
New Trends in Predictive Analytics Integration
Credit risk management, fraud detection, and compliance are increasingly being consolidated into unified platforms. This integration allows financial institutions to manage all data sources within a single ecosystem, enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of credit decisions.
One emerging trend in 2026 is the rise of Agentic AI ecosystems. These systems use multiple autonomous agents to collaboratively handle risk-related tasks. For example, Experian’s enhanced Ascend Platform employs meta-agents to calculate financial ratios and summarize results, which are then reviewed by human experts.
Another shift is the move from static data checks to real-time data orchestration. This approach continuously monitors borrower behavior and market conditions, enabling financial institutions to make decisions based on up-to-the-minute information. In environments like FedNow, this real-time capability can prevent fraud by analyzing behavioral patterns and intervening before funds are transferred.
Adding to this, climate risk integration is gaining traction. Predictive models now factor in physical climate risks – like flooding or extreme weather events – as key indicators for default prediction. Generative AI tools are also making a difference; pilot programs have shown they can cut the time needed to complete climate risk questionnaires for commercial clients by 90%, reducing the process from over two hours to less than 15 minutes.
For businesses aiming to protect themselves from credit defaults, combining predictive analytics with traditional risk mitigation tools is proving effective. CreditInsurance.com offers resources on how credit insurance and accounts receivable insurance can complement modern analytics, helping businesses build stronger financial risk management strategies.
Future Outlook for Credit Default Predictions
Over the next five years, the financial industry is expected to shift toward "accountable intelligence" – AI that not only delivers measurable ROI but also integrates seamlessly and safely into core workflows. As Alex Kwiatkowski, Director of Global Financial Services at SAS, put it:
In 2026, trust will morph from a promise to a performance metric as banks shift from model-driven to proof-driven intelligence.
Explainable AI (XAI) will play a critical role in meeting regulatory demands. Frameworks like Regulation B and Basel IV require models to provide clear, defensible reasons for credit decisions instead of relying on "black box" predictions. Joe Oleksak from Plante Moran summed it up:
If you can’t inventory, validate, monitor, and explain it, you rent the risk.
To align with these needs, institutions are adopting the NIST AI Risk Management Framework, which provides a standardized approach for managing AI risks. Contracts with AI vendors are also evolving to include strict requirements for transparency, testing, and incident management.
Despite the progress, 67% of financial institutions lack internal generative AI capabilities. To address this, many are creating cross-functional Centers of Excellence to bridge gaps in AI expertise and regulatory knowledge.
Looking ahead, 89% of financial leaders believe AI will influence every stage of the lending lifecycle, from application processing to underwriting and portfolio management. Success will depend on treating AI as a strategic asset – investing in data quality, governance, and human oversight to ensure predictive analytics deliver both performance and accountability.
sbb-itb-b840488
Conclusion: What Businesses Should Know
Advantages of Using Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics powered by AI goes beyond traditional credit scoring methods by uncovering complex, non-linear behavioral patterns that tools like FICO often overlook. This capability significantly lowers default risks, offering businesses a more precise way to manage credit. For example, advanced models like XGBoost have achieved Kolmogorov–Smirnov scores as high as 74.05% in specific arrears categories, outperforming traditional logistic regression methods. These advancements help strengthen credit risk management strategies.
In addition to reducing risk, AI automates repetitive tasks such as credit limit reviews and follow-up schedules. This automation not only cuts operational costs but also minimizes human error and provides real-time insights into payment behaviors, improving cash flow predictability. Another key benefit is the elimination of subjective bias, ensuring consistent and fair credit decisions. Modern AI systems even analyze unstructured data – like news, social media trends, or loan assessments – to enhance decision-making accuracy.
Steps Businesses Can Take
To leverage these benefits, businesses can take a few practical steps to integrate predictive analytics into their operations without overhauling existing systems. Start by segmenting your credit portfolio into arrears categories (e.g., 1–30 days, 31–90 days) and applying predictive models tailored to each range, as their effectiveness varies by delinquency stage. When selecting AI tools, focus on those that can integrate easily with your ERP and CRM systems. This ensures a smooth data flow and reduces the need for manual data entry.
Consider implementing a "human-in-the-loop" approach where AI provides confidence levels for credit decisions. This allows your team to concentrate on high-risk or uncertain cases. Tools like SHAP or LIME can help explain AI-driven decisions, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and fostering trust among stakeholders. For businesses exploring their options, CreditInsurance.com offers resources to help align predictive analytics with broader financial risk management strategies. These include credit insurance and accounts receivable insurance solutions that complement modern analytics tools.
Whiteboard series – How AI and ML are revolutionizing credit risk modeling?
FAQs
How does using real-time data enhance credit risk management?
Real-time data integration is reshaping credit risk management by making continuous monitoring and early detection of risks possible. With access to live data streams – like borrower activity and shifts in economic conditions – AI-powered systems can spot warning signs early. This gives financial institutions a crucial window to act before defaults happen, minimizing losses and enhancing decision-making.
On top of that, real-time data keeps institutions aligned with regulatory standards such as IFRS 9 and CECL. By relying on the latest information, these systems provide accurate assessments and allow lenders to adjust swiftly to evolving borrower behavior and market shifts, which is especially critical during economic challenges.
How do machine learning models like XGBoost help predict credit defaults?
Machine learning models, such as XGBoost, are crucial in predicting credit defaults. They stand out for their ability to analyze large and complex datasets with impressive precision. These models are particularly adept at identifying patterns in borrower behavior, including factors like payment history, credit utilization, and other risk indicators.
What sets XGBoost apart is its capacity to handle nonlinear relationships within data while focusing on the most important features. This makes it an invaluable tool for financial institutions looking to evaluate credit risk with greater accuracy. By using insights from XGBoost, businesses can make smarter lending decisions and reduce the likelihood of financial losses.
What are the main challenges financial institutions face when using AI for credit risk management?
Financial institutions face several hurdles when using AI for credit risk management. One major concern is the complexity of AI systems, which can lead to risks such as data privacy breaches, algorithmic bias, and a lack of transparency in how decisions are made. To address these issues, institutions need strong frameworks to ensure compliance and effectively reduce potential risks.
Another significant challenge lies in managing fragmented and inconsistent data, which makes training and validating AI models more difficult. Integrating AI into existing systems while staying within regulatory boundaries is no small feat. On top of that, as AI-driven fraud and cyber threats grow more sophisticated, organizations must prioritize real-time monitoring and controls to tackle these risks quickly and effectively.
Striking the right balance between innovation, risk management, and meeting regulatory requirements is no easy task. To succeed, institutions must implement clear governance and oversight practices when using AI for credit risk management.


