Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) is reshaping how credit histories are managed by offering a decentralized, tamper-proof system that eliminates inefficiencies in outdated credit reporting methods. Here’s what you need to know:
- Real-Time Updates: DLT ensures that credit information is updated instantly, reducing delays that often take days in older systems.
- Tamper-Resistant Records: Every credit transaction is permanently recorded and cryptographically secured, reducing errors and fraud.
- Streamlined Verification: Smart contracts automate processes, cutting costs and eliminating manual steps.
- Improved Data Access: Authorized users can access synchronized credit data without relying on centralized databases.
For businesses, this means faster decision-making, reduced financial risks, and fewer compliance headaches. DLT simplifies credit assessments, making it easier to evaluate financial risks while maintaining data security and privacy. However, companies must ensure compliance with regulations like the FCRA and GDPR to address privacy concerns and data management standards.
What is DLT and why does it matter to payment leaders? DLT Essentials
sbb-itb-b840488
Problems with Traditional Credit Histories
Centralized credit reporting systems present major challenges for businesses trying to accurately assess financial risk. These systems rely on fragmented, proprietary databases, forcing businesses to juggle multiple platforms to gather information. Service providers often guard their networks and data as private assets, creating closed ecosystems that block the exchange of information. These inefficiencies highlight the need for new solutions, such as Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT).
Data Silos and Errors
The problem isn’t just about inconvenience – fragmentation can lead to serious consequences. Errors in credit reports can prevent individuals from accessing loans, mortgages, or contracts. Centralized bureaus provide lenders with customized credit scores, but these scores are based on data that consumers have no way to verify or control. This lack of transparency results in inconsistent and unreliable information, undermining trust for everyone involved. Dmitri Gourfinkel and Álvaro Fernández, Senior Governance Specialists at the World Bank, explain:
"Without clear trails, funds can vanish with no accountability".
Even worse, centralized systems are prone to breaches and inaccuracies, making them a frequent source of consumer complaints. In fact, credit bureaus generate the highest volume of complaints to the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau. By comparison, DLT-based systems have shown an 83% reduction in error rates when measured against traditional manual credit processes.
Delayed Updates
Errors aren’t the only issue – delays in updates also compromise the reliability of credit data. Traditional systems often take 5–7 days to process updates, meaning lenders and businesses are working with outdated information. This lag creates a significant risk, especially for businesses managing multiple trade credit relationships. Companies may unknowingly extend credit to customers whose financial situations have worsened, leaving them exposed to unnecessary risk.
Expensive Verification Processes
Verification in centralized systems is another pain point, driving up costs through manual processes and administrative overhead. DLT, with its ability to perform real-time checks and automate processes, can reduce these costs by as much as 50%. Bruce Roberts, Head of Business Development for Cleared Derivatives at ION, puts it simply:
"The operational effectiveness of the collateral transfer process is far from optimal".
Manual audits and human-dependent administrative tasks not only inflate costs but also increase the likelihood of errors. This creates a system that’s both costly and unreliable, further emphasizing the need for more efficient alternatives.
How DLT Improves Credit History Transparency
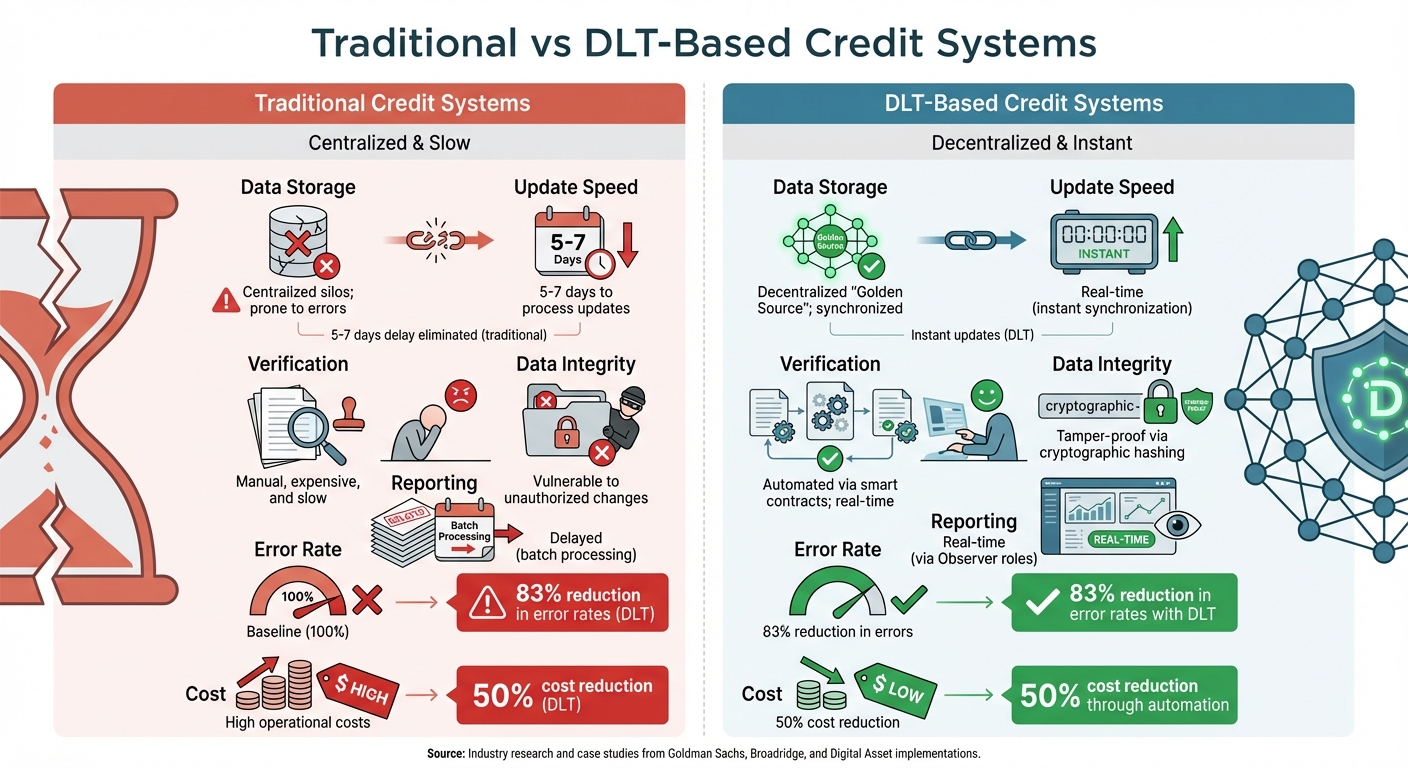
Traditional vs DLT-Based Credit Systems Comparison
DLT (Distributed Ledger Technology) addresses the flaws of traditional credit systems by offering streamlined, secure, and transparent solutions. It consolidates scattered credit data into a tamper-resistant, real-time ledger. Instead of relying on fragmented databases, DLT provides a single, unchangeable record accessible to authorized users. This eliminates the need for cumbersome data transfers and manual reconciliation.
Permanent and Tamper-Proof Records
One of DLT’s standout features is its ability to create permanent, tamper-proof records. Each entry in the ledger is assigned a unique cryptographic hash, which immediately flags any attempts at tampering. This creates an unalterable audit trail, allowing every change to a credit record to be traced back to its source.
In November 2025, researchers at Xi’an Jiaotong University and the Key Laboratory of High-Performance Distributed Ledger Technology introduced the VeriCred system. This system combines automated credit scoring with blockchain-based auditing, recording credit metrics and performance data immutably. This provides financial institutions with a secure way to assess credit risk while reducing computational demands. The research team highlighted:
"A distinctive blockchain layer is embedded to immutably trace data provenance and model decisions, ensuring full auditability." – Applied Sciences, MDPI
This level of security ensures reliable and immediate access to accurate credit data.
Real-Time Data Access
Unlike traditional systems, which often lag in updating information, DLT offers instant synchronization. Whenever a transaction is added, all ledger copies update simultaneously. Authorized users can view the most recent data without delay. In permissioned DLT setups, certain applications can act as "Observer" parties, enabling them to monitor transactions in real time without altering the data.
In November 2022, leading financial institutions like Goldman Sachs, Broadridge, and the Australian Securities Exchange adopted Daml smart contracts to establish a "golden source" of transaction data. This setup eliminated manual data transfers and achieved what Digital Asset described as "minimal reconciliations and zero latencies". This approach ensures consistent, high-quality data that is always up-to-date and free from duplication.
Faster Verification
DLT also simplifies the verification process, cutting costs and reducing the need for intermediaries. By using smart contracts, businesses can verify credit data directly, bypassing manual steps and ensuring accuracy. The system maintains a "golden source" of data automatically.
| Feature | Traditional Credit Systems | DLT-Based Credit Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Data Storage | Centralized silos; prone to errors | Decentralized "Golden Source"; synchronized |
| Verification | Manual, expensive, and slow | Automated via smart contracts; real time |
| Data Integrity | Vulnerable to unauthorized changes | Tamper-proof via cryptographic hashing |
| Reporting | Delayed (batch processing) | Real time (via Observer roles) |
The benefits are clear. By providing synchronized, permissioned data access, DLT eliminates the reconciliation delays and inefficiencies of traditional systems. As noted by Digital Asset:
"There are no ETLs needed and no reconciliations. The data is of the highest quality, is fully consistent, and is available in real time." – Digital Asset
Using DLT in Trade Credit Insurance
Trade credit insurance providers can use distributed ledger technology (DLT) to simplify risk assessments and improve data accuracy. A synchronized ledger allows insurers to avoid expensive reconciliations and quickly evaluate risks when underwriting policies or handling claims.
Tokenized Credit Histories
Credit histories can be transformed into tokenized records using cryptographic identifiers, like Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs), to represent business details or payment aliases on a blockchain. This method ensures records are portable, always up-to-date, and accessible based on authorization levels. Each party maintains a synchronized copy of the data without needing manual transfers.
Smart contracts enhance this system by enforcing privacy rules, allowing only relevant risk information to be shared. Additionally, credit data can remain physically separated across different jurisdictions, satisfying data domicile requirements, while staying synchronized through an interoperability layer.
Together, tokenization and smart contracts bring a streamlined approach to managing credit histories.
Smart Contracts for Automated Risk Assessment
Smart contracts can handle the entire credit process – from issuing policies and processing payments to detecting fraud and managing claims – through automation. For example, in 2020, Digital Asset and Knoldus introduced the DeCredit Platform, a decentralized application powered by Daml, designed for peer-to-peer lending. This platform uses smart contracts to automate workflows, where borrowers offer digital assets as collateral, and lenders propose interest rates based on automated risk evaluations.
Applying this model to trade credit insurance enables real-time fraud checks and credit authorizations before transactions are completed. Digital Asset highlights the benefits of this approach:
"Leveraging smart contracts in this context enables straight-through processing, resulting in significant benefits such as easier regulatory reporting, simplified management of credit data, elimination of duplicate processes, and enhanced user experience." – Digital Asset
This results in faster policy approvals, more precise premium calculations, and quicker claims processing.
For further details on how technology can improve transparency in trade credit insurance, visit the expert resources at CreditInsurance.com.
Regulatory and Compliance Requirements
Navigating the U.S. regulatory landscape for Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) is no small feat. Businesses must comply with overlapping requirements from multiple federal agencies like the CFPB, SEC, FinCEN, and IRS. Adding to the complexity are longstanding laws such as the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA).
The FCRA plays a key role in regulating how businesses handle consumer information. For instance, companies managing credit-related data must implement "Identity Theft Red Flags", as outlined in 17 CFR Part 162, and ensure proper disposal of consumer data to prevent unauthorized access. Additionally, the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act complements the FCRA by imposing specific rules on how financial institutions manage private consumer data, further increasing compliance responsibilities.
Data Privacy and Security Standards
Data privacy becomes a significant concern in DLT systems, as online identifiers – like wallet addresses, smart contract details, and transaction IDs – can qualify as personal data under laws such as the GDPR when linked to an individual. This creates a dilemma since DLT’s permanence clashes with data privacy rights, including the "right to be forgotten" and data correction.
Businesses using DLT must clearly define their legal roles. For example, entities initiating transactions with personal data often act as "controllers", while those running validator nodes may be classified as "processors". To address privacy concerns, organizations should conduct risk assessments of blockchain node locations to manage international data transfer risks. A best practice is to store sensitive personal credit information off-chain, recording only hashes or references on the ledger. This approach supports compliance with erasure and rectification requests.
The introduction of the UK Data (Use and Access) Act on June 19, 2025, has already prompted reviews of existing DLT frameworks to align with new legal standards. These privacy challenges underscore the pressing need for consistent data management practices.
Standardization and Interoperability
A lack of standardized data formats continues to slow DLT adoption in credit systems. The CFPB’s Personal Financial Data Rights rule (12 CFR Part 1033) highlights the importance of enabling consumers to securely access and share their financial data with third-party providers through standardized interfaces. For businesses, this means ensuring their DLT systems align with established standards to enable seamless cross-platform interaction.
Current regulations often avoid specifying technical infrastructures, leaving a gap in standardization for recording or transferring credit interests. DLT adoption is currently divided between two primary models: the "books and records" approach, which focuses on internal back-office optimization, and the "tokenization" model, which supports multi-entity asset transfers. This division complicates efforts to establish a unified industry standard.
Further challenges arise from the misalignment between traditional financial systems – operating on limited schedules – and DLT systems, which are designed for continuous, real-time operation (24/7/365). To navigate these hurdles, businesses should rely on existing policies to evaluate security, enforceability, and custodial risks when integrating DLT.
Conclusion: The Future of Credit Transparency with DLT
Distributed ledger technology (DLT) is reshaping how credit records are managed by creating permanent, tamper-resistant records and enabling real-time updates. This eliminates the delays that plague traditional systems. Big players like Goldman Sachs, Broadridge, and the Hong Kong Exchange have already embraced DLT-based frameworks to streamline financial reporting and cut reconciliation costs.
One of DLT’s standout benefits is its ability to lower costs. By automating reconciliations and removing intermediary fees, it aligns with expert predictions that smart contracts could eventually replace third-party credit reporting agencies. The unified ledger system also reduces the need for manual reconciliations, saving both time and money.
For businesses, especially those in competitive markets, DLT offers a way to reduce financial risks. Its traceability and verification capabilities strengthen the sustainability of lending programs, which can be particularly impactful for small and medium enterprises (SMEs). The technology’s continuous operation allows for real-time asset transfers, reducing the risks associated with market stress.
To fully benefit from DLT, companies need to focus on practical implementation. For instance, configuring reporting tools as "Observer" parties within smart contracts can automate regulatory reporting. It’s also crucial to prioritize interoperability when selecting DLT platforms, ensuring they can integrate with existing systems to ease the transition process. By breaking down data silos while maintaining strict privacy controls, DLT becomes an invaluable tool for managing sensitive credit information across multiple regions.
However, innovation must go hand-in-hand with regulatory compliance. While DLT minimizes reconciliations and enables instant data sharing, its adoption must align with established standards for privacy, security, and enforceability. Businesses that navigate these challenges effectively will gain a competitive edge through greater efficiency, cost savings, and stronger trust with partners.
For more guidance on using distributed ledger technology to improve credit transparency and reduce financial risks, visit CreditInsurance.com.
FAQs
How does distributed ledger technology (DLT) enhance the security and transparency of credit data?
Distributed ledger technology (DLT) strengthens the security and clarity of credit data by using a decentralized and tamper-resistant system. Every transaction is stored in a cryptographically secured ledger, making it nearly impossible for anyone to alter the data without proper authorization.
With this decentralized setup, all participants can access consistent, accurate, and current information. This not only builds trust but also minimizes errors. By offering a transparent and unchangeable record of credit histories, DLT enables businesses to make smarter decisions while staying aligned with regulatory requirements.
What compliance challenges do businesses face when using DLT for credit histories?
Businesses leveraging Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) for credit histories face several hurdles when it comes to compliance. A major sticking point is the immutability of blockchain records. Privacy laws like the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) grant consumers the right to correct or delete their data. However, blockchain’s permanent nature makes it tricky to accommodate these rights without implementing advanced technological solutions.
Another pressing issue is the challenge of keeping up with changing regulatory landscapes. Both U.S. and international regulations often emphasize transparency to combat fraud and money laundering. While this focus is essential, it can lead to privacy concerns and operational headaches. Companies also need to ensure data accuracy, secure user consent, and integrate DLT into their existing compliance frameworks. Achieving all of this demands substantial resources and meticulous planning.
Although DLT offers benefits like improved transparency and efficiency, ensuring its use aligns with legal and regulatory standards remains a significant obstacle for businesses in the credit reporting space.
How do smart contracts make credit verification faster and more transparent?
Smart contracts make credit verification easier by automating tasks and following predefined rules securely. This cuts down on the need for manual reviews, minimizes mistakes, and keeps credit data updated in real time on the blockchain.
With greater transparency and dependability, businesses can confidently rely on accurate credit histories while saving both time and resources. This efficient system also helps meet financial regulations and boosts the overall effectiveness of credit management.


