Blockchain is transforming global trade by replacing outdated, paper-based systems with secure, decentralized digital ledgers. This technology reduces fraud, speeds up cross-border transactions, and provides real-time tracking of goods. Key highlights include:
- Digital Documentation: Converts paper documents like bills of lading into tamper-proof digital records, reducing errors and delays.
- Smart Contracts: Automates payments and processes, cutting transaction times from days to seconds.
- Real-Time Tracking: Combines IoT sensors with blockchain to monitor goods throughout their journey.
- Customs Modernization: Streamlines customs clearance with instant document verification and fraud prevention.
- Trade Finance: Simplifies financing for businesses, especially small and medium-sized enterprises, by reducing costs and risks.
Blockchain in Global Trade and Supply Chains: Applications, Governance, and Industry Challenges
How Blockchain Reduces Trade Barriers
Cross-border trade has long been bogged down by layers of paperwork and middlemen, adding unnecessary delays and costs to transactions. Blockchain simplifies this process by introducing a shared digital ledger that authorized parties can access simultaneously. This eliminates the need for intermediaries, streamlining operations.
According to the World Trade Organization, blockchain’s ability to bridge information gaps is reshaping global trade. Its impact could be monumental – researchers Christine A. McDaniel and Hanna C. Norberg suggest that blockchain might increase global trade volumes and economic output even more than completely abolishing tariffs worldwide. Let’s dive into how digital trade documents and automated transactions are making this possible.
Digital Trade Documents
The reliance on paper documentation has been a major bottleneck in international trade. Documents like bills of lading, letters of credit, and insurance forms often require physical verification, signatures, and shipping between parties – a process that can take days or even weeks while leaving room for human error. Blockchain changes the game by converting these documents into tamper-proof digital records that all stakeholders can instantly verify.
A great example is the Global Shipping Business Network (GSBN) and its Cargo Release platform. This innovation has transformed cargo documentation from a process that used to take days into one that can now be completed in just a few hours. By September 2022, the platform had already served over 10,000 customers and tracked more than 1 million shipments. On a broader scale, McKinsey & Company estimates that adopting electronic bills of lading across the shipping industry could save $6.5 billion in direct costs.
Faster Cross-Border Transactions
In global trade, speed is everything, and blockchain delivers through smart contracts – self-executing agreements that automatically trigger transactions. By removing manual verification steps, these contracts significantly cut down processing times.
The difference is striking. For instance, a public Ethereum platform processed transactions in about 23 seconds during tests, while a private, customized blockchain brought that time down to just 2.8 seconds. These faster settlements not only eliminate delays but also provide a transparent transaction history, reducing risks. This transparency is especially beneficial for smaller companies that may lack established credit histories, enabling them to compete in international trade without relying on costly intermediaries.
Transparency and Security in Supply Chains
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing supply chain management by offering unmatched transparency and security at every stage. By replacing fragmented, isolated data systems with a shared ledger accessible to authorized stakeholders, blockchain ensures seamless data integration. This enables both forward traceability (tracking goods in real time) and backward traceability (identifying the origin of products). These capabilities are particularly useful in combating counterfeits and meeting strict regulatory standards. With this unified approach, businesses can monitor goods in real time – even as they cross international borders.
Real-Time Goods Tracking
When combined with IoT sensors, blockchain enables automatic, real-time tracking of shipments. Sensors installed on pallets can record both location and condition data directly onto the blockchain ledger as products move through the supply chain.
A great example of this is the "Track and Trace" prototype developed by Deloitte and Thingstream. Using Hyperledger Fabric and GSM sensors, the system records real-time location data on a single, unchangeable ledger as shipments pass through different countries. This ensures an accurate, tamper-proof history of the shipment’s journey.
In industries like pharmaceuticals and luxury goods, blockchain prototypes have been instrumental in consolidating shipment data across regions to verify authenticity. For instance, in February 2023, DHL and Accenture launched a serialization prototype with nodes in six locations to track medications from production to consumer, significantly reducing counterfeit risks. This is crucial, as the World Health Organization estimates that counterfeit drugs worth around $83 million are sold globally, posing serious health risks. Similarly, De Beers introduced a blockchain-based platform in May 2022 to track diamonds throughout their lifecycle, offering undeniable proof of their origin and authenticity.
Permanent Records for Fraud Prevention
Blockchain’s structure makes it a powerful tool against fraud. Each block in the chain is linked to the previous one through a unique digital fingerprint, making it nearly impossible to alter historical data. To tamper with just one record, a bad actor would need to re-mine all subsequent blocks – a process that becomes exponentially harder as the chain grows.
"Blockchain technology’s ability to support information sharing in a distributed network and create an immutable and traceable digital record of historical transactions makes it an attractive option for SCT [Supply Chain Traceability]." – Wafaa A.H. Ahmed and Bart L. MacCarthy
Every transaction on the blockchain is encrypted and digitally signed, ensuring both data integrity and sender authentication. This decentralized system eliminates single points of failure, meaning no one entity can alter records without being detected by the network.
To enhance security even further, cryptographic techniques like Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs) allow companies to verify product authenticity or compliance without exposing sensitive data. For example, a supplier can confirm that a product meets safety standards without revealing proprietary manufacturing details.
Blockchain also assigns unique digital identities to products, creating a chain of custody – a chronological record of every party that has handled an item. This chain spans both transaction details and physical custody, which is especially vital in regulated industries like pharmaceuticals and food. In these sectors, proving a product’s origin and handling history can be the difference between ensuring safety and facing disaster.
Blockchain in Customs Processes
Customs clearance has long been bogged down by manual document checks and paper-heavy workflows, which often open the door to fraud. Blockchain technology is stepping in to modernize this process by automating verification and providing customs officials with instant access to secure, unchangeable trade data. With tools like digital signatures and QR codes tied to blockchain records, customs officers can now verify documents on the spot, significantly reducing delays and errors.
By creating a shared digital ledger, blockchain connects exporters, importers, and customs authorities. Smart contracts further streamline the process by automatically clearing goods once all required documentation is validated. This integration bridges the gap between outdated customs systems and efficient, tech-driven solutions.
"The tamper-proof and decentralized nature of DLT makes it useful for breaking the silos that constrain international trade." – World Trade Organization
A 2021 survey by the World Customs Organization and World Trade Organization highlighted key advantages of blockchain in customs, such as better risk management, stronger fraud detection, and improved revenue collection. Customs officials can now access real-time data – including seller and buyer details, pricing, quantities, and insurance – directly from the source. This not only speeds up trade processes but also enhances compliance, ensuring public revenues are better protected. The following examples showcase how blockchain is reshaping customs operations.
Case Studies of Blockchain-Enabled Customs
Several real-world applications demonstrate how blockchain is transforming customs procedures. For instance, the Georgia Revenue Service employs Ethereum to issue preferential Certificates of Origin (CoOs) embedded with QR codes. Customs officials can scan these codes to instantly confirm the document’s authenticity through the blockchain ledger, eliminating the risk of forgery.
Singapore’s TradeTrust framework takes a different route, using a public blockchain to "notarize" digital trade documents. This allows both customs authorities and businesses to independently verify the authenticity and origin of documents without needing a central authority. In early 2023, this system enabled ExxonMobil Asia Pacific, Bunkerchain, and VLK to conduct the world’s first live cross-border trade using an Electronic Transferable Record (ETR), which functioned like a traditional paper Bill of Lading but with blockchain’s added security and efficiency.
Under the Australia-Singapore Digital Economy Agreement, the two countries trialed a blockchain Proof of Concept to enable seamless sharing and verification of digital documents between their customs systems. This initiative demonstrated how paperless cross-border trade could become a reality, laying the groundwork for fully automated customs processes. Similarly, IBM and Maersk‘s TradeLens platform, built on Hyperledger Fabric, allows supply chain participants – including customs authorities – to securely track containers from origin to destination while exchanging critical commercial documents in an unalterable environment.
sbb-itb-b840488
Blockchain in Trade Finance and Risk Mitigation
Trade finance has long been plagued by sluggish processing, high costs, and a $2.5 trillion funding gap as of 2022. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are particularly hard-hit, with a 45% rejection rate on financing applications, even though they account for 38% of all requests. Blockchain technology is driving change in this space by automating processes, reducing fraud, and providing lenders with real-time, reliable trade data. These advancements not only speed up financing but also enhance risk management across supply chains.
Faster Trade Financing
Blockchain simplifies trade financing by using smart contracts to execute payments automatically once predefined conditions are met, eliminating the need for manual intervention. For example, a simulation involving 200 transactions revealed a dramatic drop in processing times – from 8.4 days to just 0.2 days – and costs were slashed from $1,209 to $82 per transaction. In a notable 2016 pilot, Barclays Bank and Wave completed a trade finance transaction in just 4 hours, a process that typically takes 7 to 10 days.
This speed is possible because blockchain creates a unified data system accessible to all involved parties. Lenders can instantly verify creditworthiness and transaction performance [22, 23]. Take the World Food Programme’s "Building Blocks" system, for instance. Powered by a permissioned Ethereum network, it managed food assistance payments for Syrian refugees in Jordan while lowering transaction costs by 98% compared to traditional banking methods. By 2030, financial institutions worldwide are expected to save over $27 billion annually in cross-border settlement transactions through blockchain.
But blockchain’s impact goes beyond efficiency – it also helps tackle financial risks.
Reducing Credit and Political Risks
Blockchain’s immutable ledgers significantly cut down on fraud and errors in trade finance, offering greater transparency. This allows lenders to assess risks with more accuracy, enabling banks to fund smaller transactions that were previously considered too expensive or risky [22, 23].
Political risks are also addressed through decentralized systems. By reducing reliance on specific national banking infrastructures, blockchain minimizes exposure to regulatory disruptions. Shared ledgers give multiple banks access to verified records on exporters and importers in real time, reducing the high due diligence costs that often lead to SME financing denials. This added transparency strengthens the security and reliability of global supply chains.
Of course, blockchain cannot eliminate all credit and political risks. Businesses should consider credit insurance solutions, such as those offered at CreditInsurance.com, to safeguard against non-payment, customer insolvency, and geopolitical instability. By combining blockchain’s efficiency with robust credit insurance, companies can create a more resilient framework for managing international trade risks.
Blockchain vs. Traditional Systems
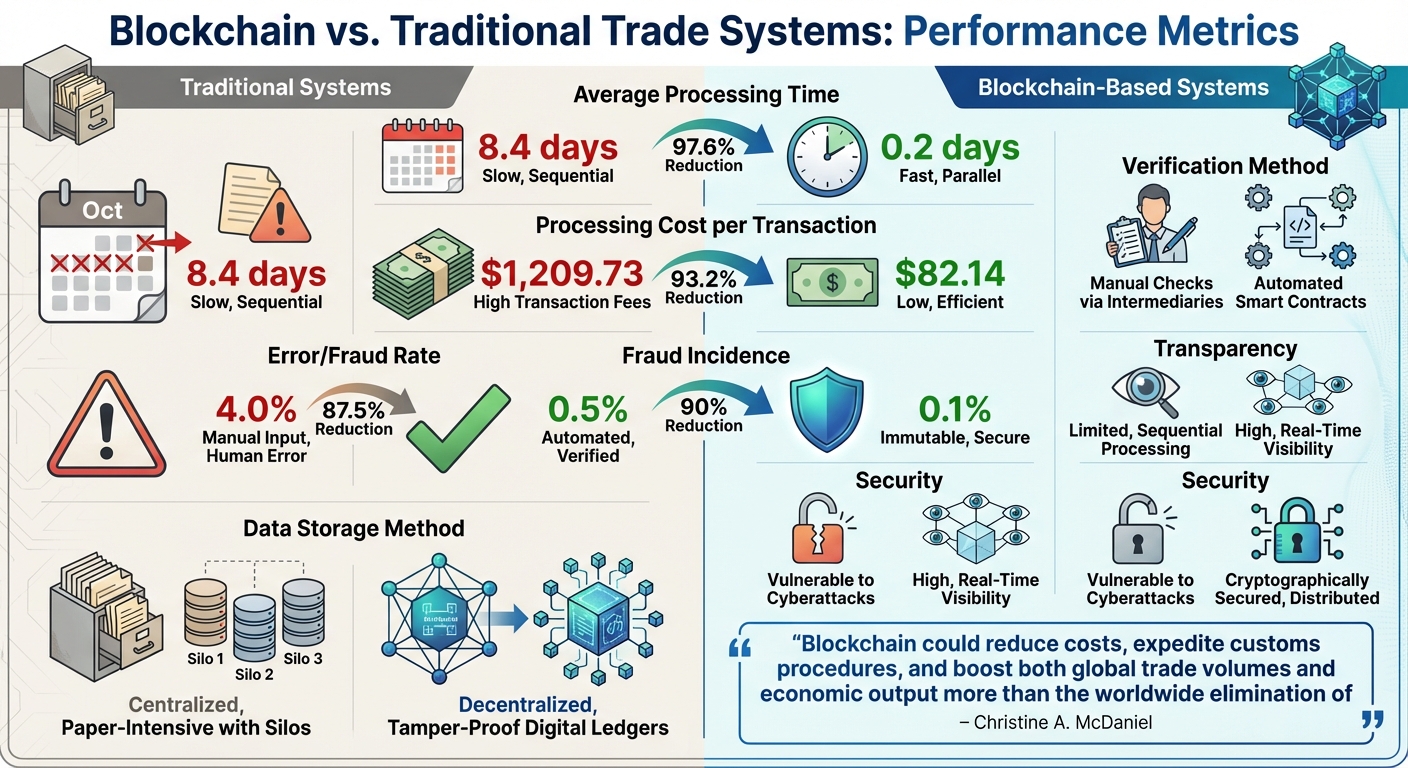
Blockchain vs Traditional Trade Systems: Performance Comparison
Traditional global trade systems rely heavily on paper documents and centralized intermediaries like banks, auditors, and customs brokers. These processes create inefficiencies, slow down operations, and drive up costs. Blockchain, on the other hand, introduces a decentralized and automated approach that eliminates many of these bottlenecks, offering a streamlined alternative for global trade.
The performance gap between these systems is striking. Blockchain has reduced average processing times from 8.4 days to just 0.2 days and cut transaction costs dramatically – from $1,209.73 to $82.14 per transaction. It has also significantly lowered error and fraud rates, with errors dropping from 4.0% to 0.5% and fraud incidents decreasing from 1.0% to 0.1%. These improvements are largely driven by features like smart contracts, which automate payments, and immutable ledgers, which ensure data integrity.
"Blockchain could reduce costs, expedite customs procedures, and boost both global trade volumes and economic output more than the worldwide elimination of tariffs." – Christine A. McDaniel, George Mason University – Mercatus Center
Another key difference lies in how data is stored and secured. Traditional systems rely on centralized databases, which are vulnerable to cyberattacks and single points of failure. In contrast, blockchain uses a decentralized, cryptographically secured structure that distributes data across multiple nodes. This makes tampering with records nearly impossible without detection. Blockchain creates what some call a "decentralized trust layer", where all participants can access and verify the same information in real time, removing the need for third-party validation.
Comparison Table: Blockchain vs. Traditional Systems
| Metric | Traditional Systems | Blockchain-Based Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Average Processing Time | 8.4 days | 0.2 days |
| Processing Cost per Transaction | $1,209.73 | $82.14 |
| Error/Fraud Rate | 4.0% | 0.5% |
| Fraud Incidence | 1.0% | 0.1% |
| Data Storage Method | Centralized; paper-intensive with silos | Decentralized; tamper-proof digital ledgers |
| Verification Method | Manual checks via intermediaries | Automated smart contracts |
| Transparency | Limited; sequential processing | High; real-time visibility for all participants |
| Security | Vulnerable to cyberattacks | Cryptographically secured, distributed |
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is transforming global trade supply chains by tackling inefficiencies that have plagued traditional systems. Its ability to provide a single, unchangeable ledger eliminates information silos and reduces the need for manual reconciliation, making cross-border trade far more efficient. This shift also opens the door for integrating blockchain with advanced risk management practices.
To make the most of blockchain’s potential, combining its transparency with strong risk management strategies is essential. The verified data that blockchain offers can enable better terms for trade credit insurance, as insurers gain access to undeniable proof of shipment and delivery. This feature is especially critical in addressing the growing global trade financing gap, which now surpasses $4 trillion.
Looking ahead, businesses can focus on specific applications like digitizing customs documents, automating payments using smart contracts, or leveraging IoT sensors for real-time tracking. Early collaboration with IT, cybersecurity, and trade experts is key to ensuring these systems are integrated smoothly. As Hélène Stanway from XL Catlin emphasized during a blockchain project with Maersk:
"With a blockchain we had that single source of the truth".
FAQs
How does blockchain enhance transparency and security in global supply chains?
Blockchain brings a new level of transparency and security to global supply chains thanks to its decentralized and tamper-resistant structure. By recording all transactions on a shared, unalterable ledger, it ensures that every participant in the supply chain has access to accurate and trustworthy data. This setup enables real-time tracking of goods, confirms their origins, and minimizes risks like fraud or data manipulation.
When it comes to security, blockchain relies on cryptographic techniques to safeguard data against unauthorized changes. Its decentralized nature removes the need for a single control point, reducing vulnerabilities to cyberattacks or system failures. These qualities enhance trust among supply chain partners and reinforce the reliability of global trade networks.
How do smart contracts help speed up cross-border trade transactions?
Smart contracts simplify international trade by automating crucial processes, cutting out the need for middlemen, and providing a secure, transparent framework for transactions. By turning agreements into digital formats, they remove the hassle of manual paperwork and help avoid lengthy administrative delays.
These self-executing contracts boost efficiency by automatically enforcing terms as soon as the agreed conditions are met. This reduces the chances of errors or disputes, speeds up transactions, and fosters trust between trading partners, making global trade more seamless and dependable.
How does blockchain help small and medium-sized businesses access trade financing?
Blockchain is transforming how small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) access trade financing by offering greater transparency, enhanced security, and streamlined efficiency in financial transactions. Its decentralized and tamper-resistant system gives lenders a reliable record of transactions, helping SMEs demonstrate their creditworthiness more effectively.
This technology also speeds up processes like document verification and compliance, reducing the delays and expenses often tied to international trade. By tackling issues such as high transaction costs and trust barriers, blockchain opens the door for financial institutions to provide credit to SMEs that might otherwise face challenges in securing funding. This allows more businesses to engage in global trade with increased confidence and fewer obstacles.


