Credit risk management helps businesses prevent losses from defaults and non-payments by evaluating customers, setting credit limits, and monitoring payments. Market volatility, driven by factors like inflation, interest rate changes, and geopolitical events, directly affects credit risk by destabilizing customers’ financial health. Stable markets allow businesses to rely on historical data and fixed credit policies, but these methods often fail during volatile periods, where unpredictable changes demand flexible, real-time strategies.
Key Takeaways:
- Stable markets: Credit scoring, historical data, and fixed policies work well.
- Volatile markets: Rising defaults, fluctuating credit spreads, and economic shocks require dynamic strategies.
- Dynamic strategies: Real-time monitoring, scenario modeling, and pre-set triggers help businesses respond quickly.
- Tools like trade credit insurance protect cash flow and support growth even in uncertain conditions.
In turbulent times, businesses must shift from static to dynamic credit risk management to safeguard finances and seize opportunities.
The Hidden Forces Driving Credit Spread Volatility in Unstable Markets
Managing Credit Risk in Stable Markets
Stable markets offer a more predictable landscape for managing credit risk. These periods are typically characterized by steady economic growth, low inflation, and monetary policies that encourage stability. In such an environment, businesses can rely on historical data to anticipate future trends. As Janet L. Yellen, former Federal Reserve Governor, explained:
"Credit scoring – which is a statistical procedure that provides an estimate of default probability for each potential loan – increasingly is being used for small business lending and middle-market commercial lending".
This predictability enables companies to adopt standardized methods for risk management. By the mid-1990s, around 60% of the top 50 banks were already using internal systems to allocate capital based on specific risk grades for commercial loans. These practices are effective in stable markets, where loss distributions remain consistent over time. Credit scorecard models thrive in these conditions because they rely on historical loss data from similar loans. However, their reliability diminishes when market dynamics shift. Below are examples of how businesses approach credit risk in stable environments.
Predictable Payment Patterns and Fixed Credit Policies
Stable markets bring consistent debtor behavior, which simplifies risk assessment. Customers are more likely to pay on time, allowing businesses to manage cash flow efficiently and establish fixed credit policies. This reliability also makes it possible to extend payment terms and reduce reserve requirements. The 5 Cs of Credit – Character, Capacity, Capital, Collateral, and Conditions – become particularly effective tools in these scenarios, as a borrower’s past behavior serves as a strong indicator of future creditworthiness.
Moreover, stability allows for standardization. By relying on established metrics, companies can streamline underwriting processes and reduce costs. These metrics often require less frequent updates, saving time and resources.
Drawbacks of Fixed Risk Management Methods
While fixed credit policies work well in stable conditions, they have notable limitations. These methods are heavily tied to historical trends, which can become outdated when markets shift. Risk thresholds set during periods of low interest rates and minimal volatility may leave businesses exposed when economic conditions change. As McKinsey experts Kirtiman Pathak, Christophe Rougeaux, and Himanshu Singh observed:
"The reasonable assumption is that the business cycle has shifted, and through-the-cycle portfolio behavior may significantly change".
Another challenge is the inability of fixed methods to account for sudden disruptions. Traditional metrics, often updated quarterly, may fail to capture rapid changes caused by geopolitical events, supply chain issues, or unexpected economic shocks. When market volatility disrupts established relationships, these models often struggle to adapt, leaving businesses vulnerable. Companies that grow too comfortable with stable conditions risk being unprepared when the environment takes an unexpected turn.
Managing Credit Risk in Volatile Markets
In volatile markets, the usual methods of credit analysis can falter, thanks to unpredictable revenue, margins, and collateral values. Industries facing high volatility often experience annual revenue swings of 10%–20%, driven by global disruptions and fluctuating commodity prices. As Brendan McErlaine of IBISWorld points out:
"Volatility magnifies credit risk by disrupting repayment capacity, reducing collateral reliability, and throwing off even well‐calibrated models".
In asset-heavy industries, the resale value of pledged equipment can shift dramatically over a single business cycle. This leaves lenders vulnerable to under-secured loans, triggering noticeable impacts on default rates and borrowing costs.
Increased Default Rates and Credit Spread Fluctuations
Market downturns are often accompanied by rising default rates. For example, in October 2025, First Brands’ bankruptcy filing caused leveraged loan spreads to rise by 10 basis points, while riskier "covenant‐lite" loans saw spreads increase by nearly 15 basis points. Additionally, when government bond yields fluctuate, they can disproportionately influence borrowing costs, especially when credit spreads make up a smaller portion of total yield.
Certain sectors carry concentrated risks that amplify these challenges. By late 2025, the "Magnificent 7" tech stocks accounted for nearly 35% of the S&P 500’s total market capitalization, a steep rise from 20% in November 2022. Valuations for these stocks reached the top 10% of their historical range. Meanwhile, consumer credit markets showed signs of strain, with credit card and auto loan delinquencies staying above pre-pandemic levels throughout late 2025.
How Economic Shocks Affect Customer Payment Ability
Economic shocks not only disrupt asset values but also weaken customers’ ability to meet payment obligations. Rising interest rates are a key factor, particularly in sectors sensitive to rate changes such as manufacturing, utilities, and technology. For instance, when mortgage refinance activity dropped nearly 45% year-over-year due to tighter financial conditions, lenders had to shift focus from originating loans to servicing and mitigating losses.
Inflation introduces a different set of hurdles. Sharp price increases in essentials like food, utilities, and rent reduce consumers’ disposable income while simultaneously driving up business operating costs. On top of that, trade disputes and geopolitical instability can trigger sudden supply chain disruptions and commodity price spikes. A case in point: in 2022, Australian construction firm Clough entered administration after cost overruns on major infrastructure projects – caused by soaring steel and energy prices – wiped out their cash flow and ability to repay debt. Similarly, TGI Fridays filed for bankruptcy in late 2024, citing a combination of COVID-19 shutdowns, macroeconomic pressures, and shifting consumer spending patterns tied to rising interest rates.
The gradual withdrawal of fiscal support has also exposed credit vulnerabilities that were previously masked by government relief programs. Arif Husain, Global Head of Fixed Income at T. Rowe Price, highlights the broader issue:
"We don’t have a U.S. government debt problem; we have a global government debt problem. This needs funding, and who will buy bonds with all that duration risk if they don’t pay much above cash?"
This funding gap adds further pressure on corporate borrowers. As bond market volatility widens credit spreads, the cost of capital rises across industries, creating a challenging environment for debt management.
sbb-itb-b840488
Static vs. Dynamic Risk Management Strategies
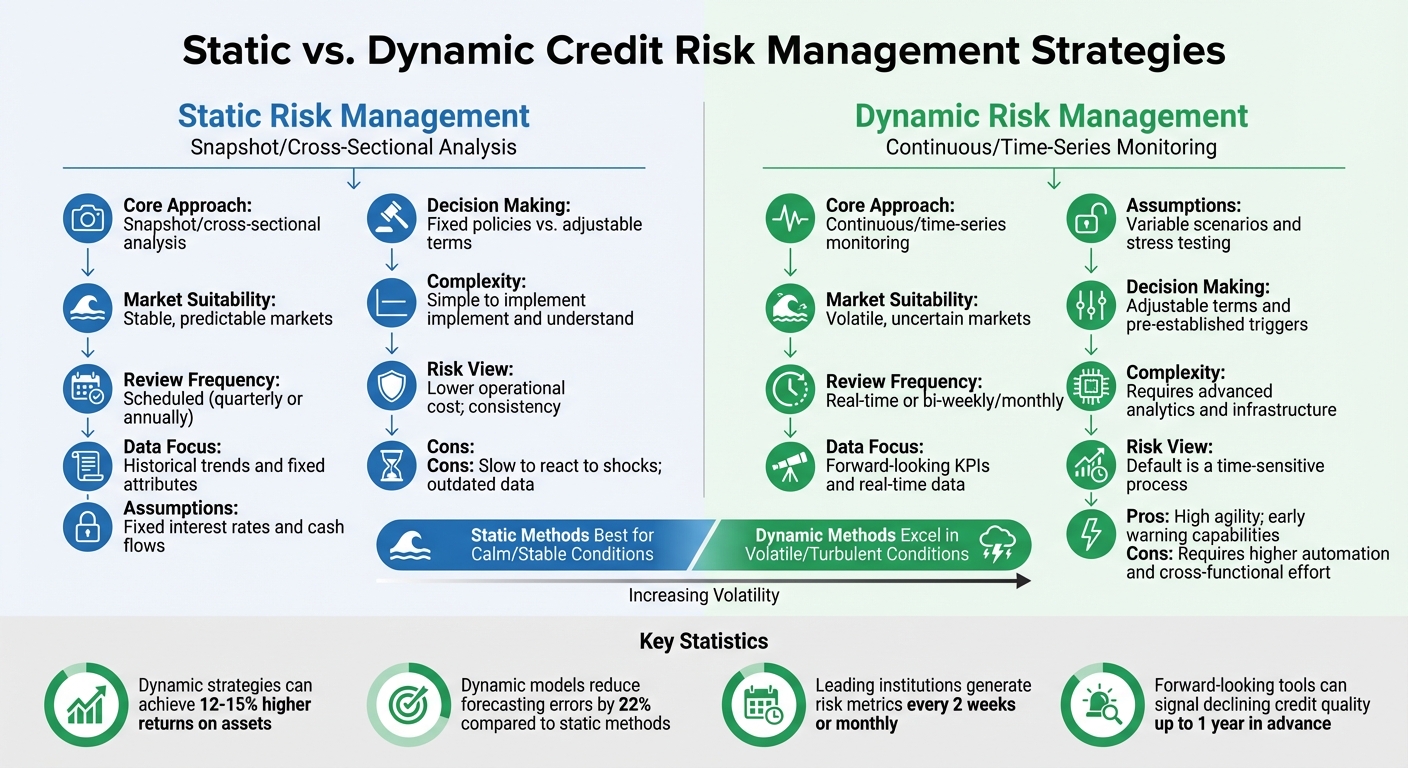
Static vs Dynamic Credit Risk Management Strategies Comparison
When it comes to managing risk, two main approaches stand out: static and dynamic strategies. Static strategies rely on historical data, offering a snapshot of risk based on past conditions, while dynamic strategies continuously adapt to real-time data. These methods address the limitations of traditional models and provide tailored solutions for varying market scenarios.
Static Strategies: Best for Predictable Markets
Static risk management shines in stable and predictable environments. It works well when payment patterns are consistent, and market correlations remain steady. These strategies depend on periodic reviews and standard macroeconomic indicators, making them straightforward to implement and maintain. Their simplicity ensures consistency in credit decisions and minimizes technological complexity.
However, static models have a glaring limitation: they struggle to account for changes over time. As Dennis Glennon and Peter Nigro point out in The Journal of Credit Risk:
"Static-scoring models are not designed to capture the effect of time (ie, seasoning) on the likelihood of default".
This means that when markets shift unexpectedly, institutions relying solely on static models can find themselves stuck with outdated assumptions. McKinsey highlights this challenge:
"The historical data used to support credit decisions often do not compute in the current context".
Dynamic Strategies: Necessary for Volatile Markets
Dynamic risk management, on the other hand, is designed for volatile and unpredictable markets. These strategies involve continuous monitoring, flexible time horizons, and detailed scenario modeling to adapt quickly to changing conditions. Leading institutions now generate risk metrics every two weeks or monthly, enabling proactive decision-making. Forward-looking tools can even signal declining credit quality up to a year in advance.
A compelling example comes from March 2025, when a Midwest bank with $50 billion in assets used dynamic strategies to enhance its net interest margin. By employing machine learning to analyze deposit repricing, the bank discovered that 40% of its savings accounts were rate-insensitive. Acting on this insight, they reduced promotional rates by 75 basis points and hedged $300 million in agency callables using Monte Carlo simulations. Over 18 months, this approach expanded their net interest margin by 22 basis points and reduced economic value of equity volatility from 12% to 7%. As Himanshu Jain, a Data & AI Commercialization Specialist, explains:
"Dynamic ALM transcends regulatory compliance to become a strategic profit engine".
Dynamic strategies also rely on pre-established triggers – preset actions that activate automatically when specific risk thresholds are crossed. These could include adjusting portfolio allocations, refining collections processes, or tightening credit terms for certain customer groups. By optimizing asset-liability mismatches, banks using dynamic methods can achieve 12–15% higher returns on assets. This demonstrates the importance of agility in managing risk during turbulent times.
Comparison Table: Static vs. Dynamic Methods
| Feature | Static Risk Management | Dynamic Risk Management |
|---|---|---|
| Core Approach | Snapshot/cross-sectional analysis | Continuous/time-series monitoring |
| Market Suitability | Stable, predictable markets | Volatile, uncertain markets |
| Review Frequency | Scheduled (quarterly or annually) | Real-time or bi-weekly/monthly |
| Data Focus | Historical trends and fixed attributes | Forward-looking KPIs and real-time data |
| Assumptions | Fixed interest rates and cash flows | Variable scenarios and stress testing |
| Decision Making | Fixed policies vs. adjustable terms | Adjustable terms and pre-established triggers |
| Complexity | Simple to implement and understand | Requires advanced analytics and infrastructure |
| Risk View | Probability of default is constant | Default is a time-sensitive process |
| Pros | Lower operational cost; consistency | High agility; early warning capabilities |
| Cons | Slow to react to shocks; outdated data | Requires higher automation and cross-functional effort |
Regulatory frameworks like Basel III and IFRS 9 are accelerating the adoption of dynamic strategies. These frameworks require banks to hold capital against risk-weighted assets that respond to real-time credit rating changes. Additionally, dynamic models, such as Long Short-Term Memory networks for liquidity forecasting, have been shown to outperform static methods like ARIMA, reducing errors by 22%. This shift underscores the growing importance of real-time, adaptive risk management in today’s banking landscape.
Using Trade Credit Insurance During Market Volatility
In uncertain markets, trade credit insurance does more than just provide a safety net – it becomes a strategic advantage. Consider this: trade credit insurance supports nearly $9.5 trillion in global trade transactions every year. It shields businesses from risks that spike during volatile times, such as customer defaults, late payments, or insolvency.
As Marsh highlights:
"Traditional risk models, which rely on historical data, often don’t capture the rapid market shifts caused by evolving trade policies, leaving companies and lenders potentially exposed to unforeseen credit risks".
This is where trade credit insurance steps in, bridging the gap by offering protection that evolves alongside market conditions. However, businesses should be aware that insurers may limit or even withdraw coverage for high-risk industries during severe downturns. This reality underscores the importance of using trade credit insurance not just as a safety measure but as a proactive tool to safeguard cash flow, even in challenging times.
Protecting Cash Flow with Insured Receivables
Insured receivables play a crucial role in maintaining steady cash flow, even when customers face financial challenges. Whether it’s inflation, rising interest rates, or supply chain disruptions, these protections ensure that income streams remain secure. This coverage doesn’t stop at customer transactions – it also extends to supplier agreements, shielding businesses from losses if suppliers fail to meet their commitments.
To stay ahead of potential risks, businesses should keep an eye on forward-looking indicators like customer liquidity, leverage, and sudden changes in working capital. These insights can help predict delinquencies before they occur, providing valuable time to mitigate risks.
Supporting Growth and Financing Options
Beyond protection, trade credit insurance opens doors to growth. It allows businesses to offer competitive credit terms to customers without taking on undue risk. Insured receivables also serve as high-quality collateral, reducing lender risk and improving access to financing. This can be especially critical during periods when traditional loans are harder to secure, enabling companies to seize opportunities even in turbulent times.
This alignment of risk management with broader business strategies can also position companies for mergers and acquisitions during volatile periods. As Oliver Jones, EY-Parthenon Global Strategy and Transactions Markets Leader, puts it:
"Viewing strategic decision-making through the lens of geopolitical and other risks puts companies in a stronger position to drive organic and inorganic growth".
By protecting growth and ensuring financing flexibility, trade credit insurance becomes a key ally in navigating market uncertainty.
Adjusting Insurance Policies for Changing Conditions
In volatile markets, static insurance policies simply don’t cut it. Businesses need flexible, responsive coverage to keep up with rapid changes. This involves working closely with insurers to adjust coverage limits, revise terms for specific customers, and account for emerging risks.
Modern tools like AI-driven analytics and tariff simulators are making it easier to adapt. These technologies use real-time data and stress tests to help businesses quickly reassess credit exposure when trade policies shift or new geopolitical risks arise. Additionally, conducting regular due diligence on both direct and indirect suppliers is essential to ensure they remain financially stable and capable of withstanding market shocks.
Open communication with insurance providers is also vital. Insurers often identify emerging risks in specific industries or regions and may reduce or withdraw coverage accordingly. Businesses that stay ahead of these changes and have contingency plans ready can use their policies as dynamic tools rather than rigid contracts.
For more insights on maximizing the benefits of trade credit insurance during market volatility, visit our resources at CreditInsurance.com.
Conclusion: Managing Credit Risk in Different Market Conditions
Credit risk strategies that work well in steady markets can falter when faced with volatility. In stable times, decisions are often guided by historical data, quarterly reviews are sufficient, and fixed credit policies keep things running smoothly. But when markets become unpredictable, relying on past performance becomes less effective. As Kirtiman Pathak from McKinsey explains:
"The historical data used to support credit decisions often do not compute in the current context. Many banking leaders are quickly realizing that new approaches are required to navigate current conditions".
This shift underscores the need for more adaptable approaches. In volatile markets, businesses benefit from dynamic strategies, which involve more frequent reviews – monthly or even bi-weekly – and stress-tested risk limits. These strategies also rely on forward-looking metrics, such as real-time tracking of liquidity, leverage, and working capital, to better anticipate and respond to market changes.
Another valuable tool in managing credit risk is trade credit insurance. It not only safeguards cash flow but also allows businesses to offer competitive credit terms. However, insurers may reduce coverage in high-risk sectors during economic downturns, making it essential to balance this tool with other risk management practices.
The bottom line? Flexibility is key in uncertain markets. By combining agile risk monitoring with the protection of trade credit insurance, businesses can not only manage challenges but also seize new opportunities. Whether the market is steady or turbulent, having the right credit risk strategy in place helps protect your bottom line and supports growth. For more guidance on adjusting credit risk strategies to market changes, visit CreditInsurance.com.
FAQs
How can businesses manage credit risk effectively in volatile markets?
Managing credit risk in unpredictable markets demands quick and strategic adjustments. By leveraging real-time data – like shifts in interest rates, currency exchange fluctuations, and customer payment behaviors – businesses can keep credit assessments current and spot potential risks before they escalate. Regularly reviewing credit policies and automatically adjusting credit limits based on economic trends and stress test results can help minimize potential financial setbacks.
Tools like advanced analytics and early-warning systems are essential in this process. These systems merge broader economic indicators, such as rising interest rates, with detailed insights into the financial health of individual customers. This enables businesses to take proactive steps, whether it’s addressing overdue invoices, prioritizing collections, or activating credit insurance to cushion against defaults. For companies in the U.S., CreditInsurance.com provides helpful resources and solutions to safeguard against non-payment risks, while also supporting growth through extended credit lines and better financing opportunities.
How does trade credit insurance help businesses during volatile markets?
Trade credit insurance shields businesses from the financial risks that come with customer defaults or payment delays – risks that tend to rise during periods of market instability. By safeguarding accounts receivable, it helps maintain steady cash flow, ensuring companies can keep up with their financial commitments, even when the market is unpredictable.
On top of that, trade credit insurance enhances access to financing by turning receivables into more dependable assets. This added reliability allows businesses to confidently extend credit lines, pursue growth opportunities, and handle market ups and downs with greater ease.
Why don’t static risk management strategies work well in volatile markets?
Static risk management strategies rely heavily on fixed assumptions and historical data, which can limit their effectiveness in fast-changing, volatile markets. When faced with sudden shifts in creditworthiness, sharp price swings, or unforeseen macroeconomic events, these rigid methods often fall short. They lack the flexibility required to adapt quickly and support timely decisions.
In contrast, businesses operating in unpredictable markets benefit from dynamic strategies that incorporate real-time data and adjust to evolving conditions. This forward-thinking approach not only helps manage risks more effectively but also ensures a stronger readiness to handle financial uncertainties.


